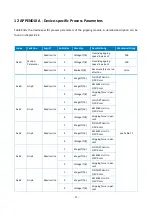
- 43 -
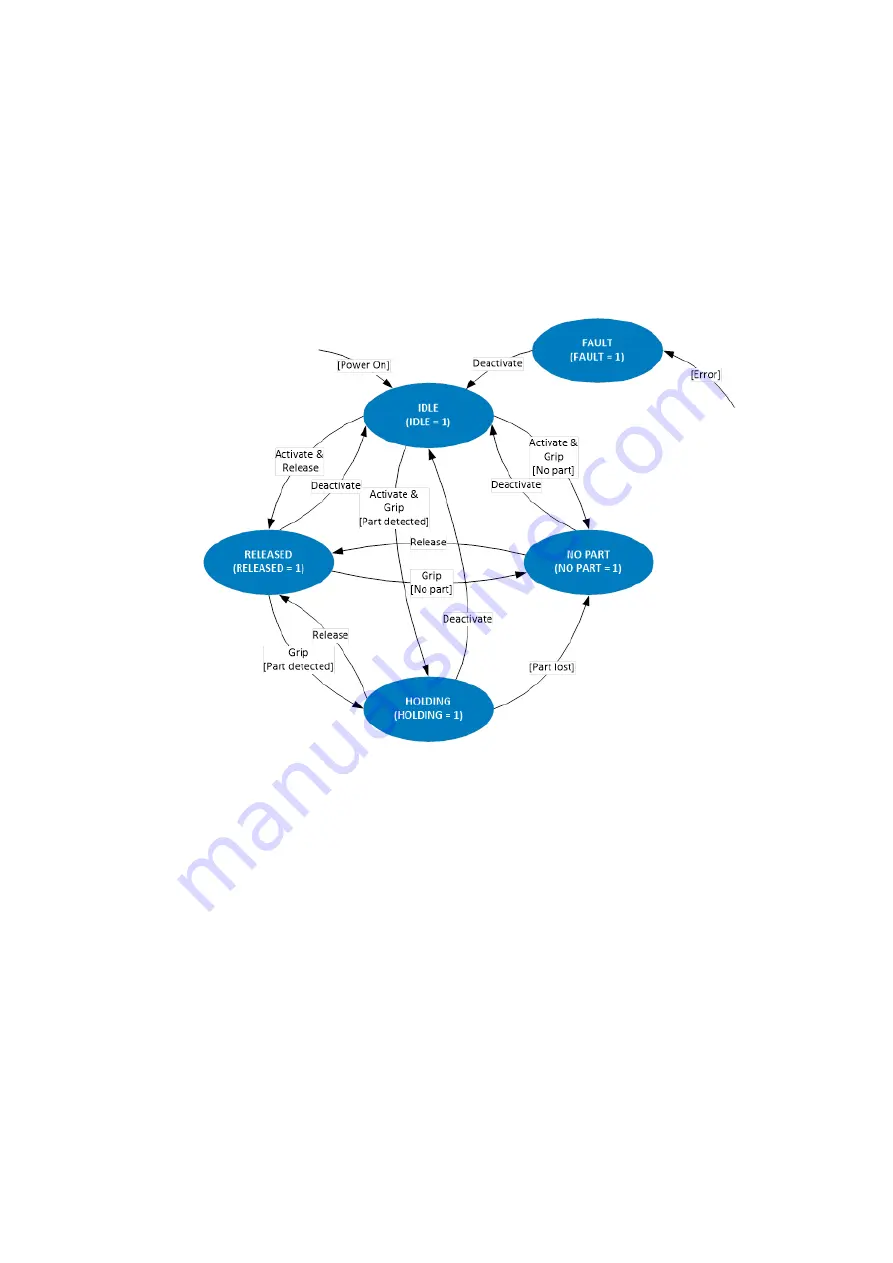
is executed and the gripping state changes accordingly. Every command leads to a change of state so the
completion of a command can be identified by waiting for a change of state.
Thus, the gripping state provides a simple opportunity to monitor the gripping process in the controlling PLC
or robot control. After a new gripping command has been issued, you must just wait for the change of the
gripping state to identify the correct or incorrect execution of the command and take the next process step
accordingly.
Figure 13: Gripping state
9.6
Parameterizable Grips
Four different grips can be parameterized for the gripping of different parts. The grip is selected via the grip
index, which is transmitted by the cyclic process data, and is performed with the gripping commands GRIP or
RELEASE.
As depicted in Figure14, for parameterization, a position window must be determined by the RELEASE Limit
and NO PART Limit for each grip. The part to be gripped must be within this window. When the base jaws are
blocked within this window during GRIPPING, the gripping module detects a valid grip and changes to the
gripping state HOLDING. When the base jaws reach the specified NO PART Limit, the gripping state changes
to NO PART to signal that no part has been gripped.