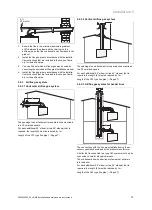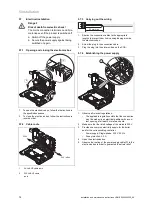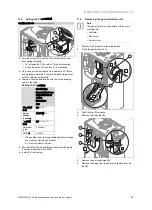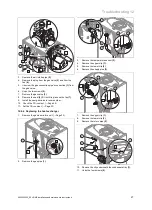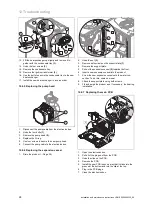
Start-up 7
0020224355_00 HOME Installation and maintenance instructions
17
7.3
Checking and treating the heating
water/filling and supplementary water
Caution.
Risk of material damage due to poor-qual-
ity heating water
▶
Ensure that the heating water is of suffi-
cient quality.
▶
Before filling or topping up the system, check the quality
of the heating water.
Checking the quality of the heating water
▶
Remove a little water from the heating circuit.
▶
Check the appearance of the heating water.
▶
If you ascertain that it contains sedimentary materials,
you must desludge the system.
▶
Use a magnetic rod to check whether it contains mag-
netite (iron oxide).
▶
If you ascertain that it contains magnetite, clean the sys-
tem and apply suitable corrosion-protection measures, or
fit a magnet filter.
▶
Check the pH value of the removed water at 25 °C.
▶
If the value is below 6.5 or above 8.5, clean the system
and treat the heating water.
▶
Ensure that oxygen cannot get into the heating water.
(
→
Page 20)
Checking the filling and supplementary water
▶
Before filling the system, measure the hardness of the
filling and supplementary water.
Treating the filling and supplementary water
▶
Observe all applicable national regulations and technical
standards when treating the filling and supplementary
water.
Provided the national regulations and technical standards
do not stipulate more stringent requirements, the following
applies:
You must treat the heating water in the following cases:
–
If the entire filling and supplementary water quantity dur-
ing the operating life of the system exceeds three times
the nominal volume of the heating installation, or
–
If the guideline values listed in the following table are not
met, or
–
if the pH value of the heating water is less than 6.5 or
more than 8.5.
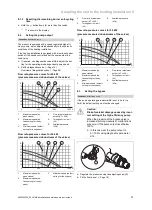
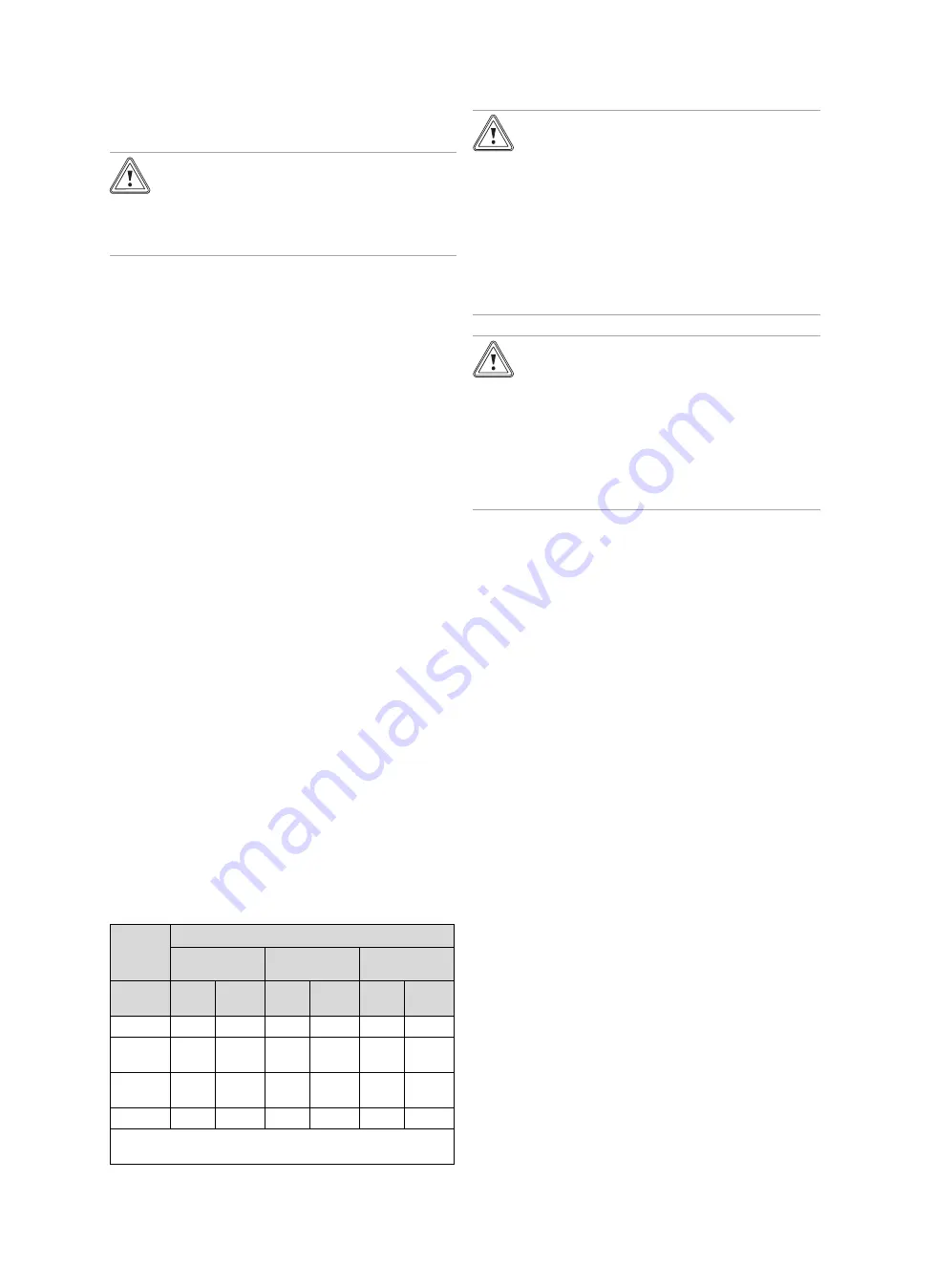
Total
heating
output
Water hardness at specific system volume
1)
≤
20 l/kW
> 20 l/kW
≤
50 l/kW
> 50 l/kW
kW
ppm
CaCO
₃
mol/
m
³
ppm
CaCO
₃
mol/
m
³
ppm
CaCO
₃
mol/
m
³
< 50
< 300
< 3
200
2
2
0.02
> 50
to
≤
200
200
2
150
1.5
2
0.02
> 200
to
≤
600
150
1.5
2
0.02
2
0.02
> 600
2
0.02
2
0.02
2
0.02
1) Nominal capacity in litres/heating output; in the case of multi-
boiler systems, the smallest single heating output is to be used.
Caution.
The use of unsuitable heating water may
cause aluminium corrosion and a result-
ing lack of leak-tightness.
In contrast to steel, grey cast iron or copper,
for example, aluminium reacts with alkaline
heating water (pH value > 8.5) to produce
substantial corrosion.
▶
When using aluminium, make sure that
the pH value of the heating water is
between 6.5 and a maximum of 8.5.
Caution.
Risk of material damage if the heating
water is treated with unsuitable additives.
Unsuitable additives may cause changes in
the components, noises in heating mode and
possibly subsequent damage.
▶
Do not use any unsuitable frost and cor-
rosion protection agents, biocides or seal-
ants.
No incompatibility with our products has been detected to
date with proper use of the following additives.
▶
When using additives, follow the manufacturer's instruc-
tions without exception.
We accept no liability for the compatibility of any additive or
its effectiveness in the rest of the heating system.
Additives for cleaning measures (subsequent
flushing required)
–
Fernox F3
–
Sentinel X 300
–
Sentinel X 400
Additives intended to remain permanently in the
system
–
Fernox F1
–
Fernox F2
–
Sentinel X 100
–
Sentinel X 200
Additives for frost protection intended to remain
permanently in the system
–
Fernox Antifreeze Alphi 11
–
Sentinel X 500
▶
If you have used the above-mentioned additives, inform
the operator about the measures that are required.
▶
Inform the operator about the measures required for frost
protection.
Summary of Contents for home combi
Page 51: ......