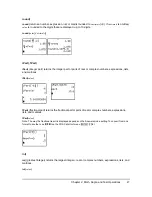
f
′
x
( )
f x
ε
+
(
)
f x
ε
–
(
)
–
2
ε
------------------------------------------
=
Chapter 2: Math, Angle, and Test Operations
41
MathPrint™:
Classic:
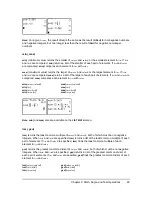
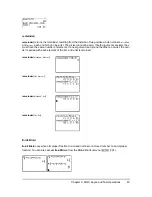
nDeriv(
expression
,
variable
,
value
[
,
H
]
)
nDeriv(
uses the symmetric difference quotient method, which approximates the numerical
derivative value as the slope of the secant line through these points.
As
H
becomes smaller, the approximation usually becomes more accurate. In MathPrint™ mode,
the default
H
is 1
E
M
3. You can switch to Classic mode to change
H
for investigations.
You can use
nDeriv(
once in
expression
. Because of the method used to calculate
nDeriv(
, the TI-84
Plus can return a false derivative value at a nondifferentiable point.
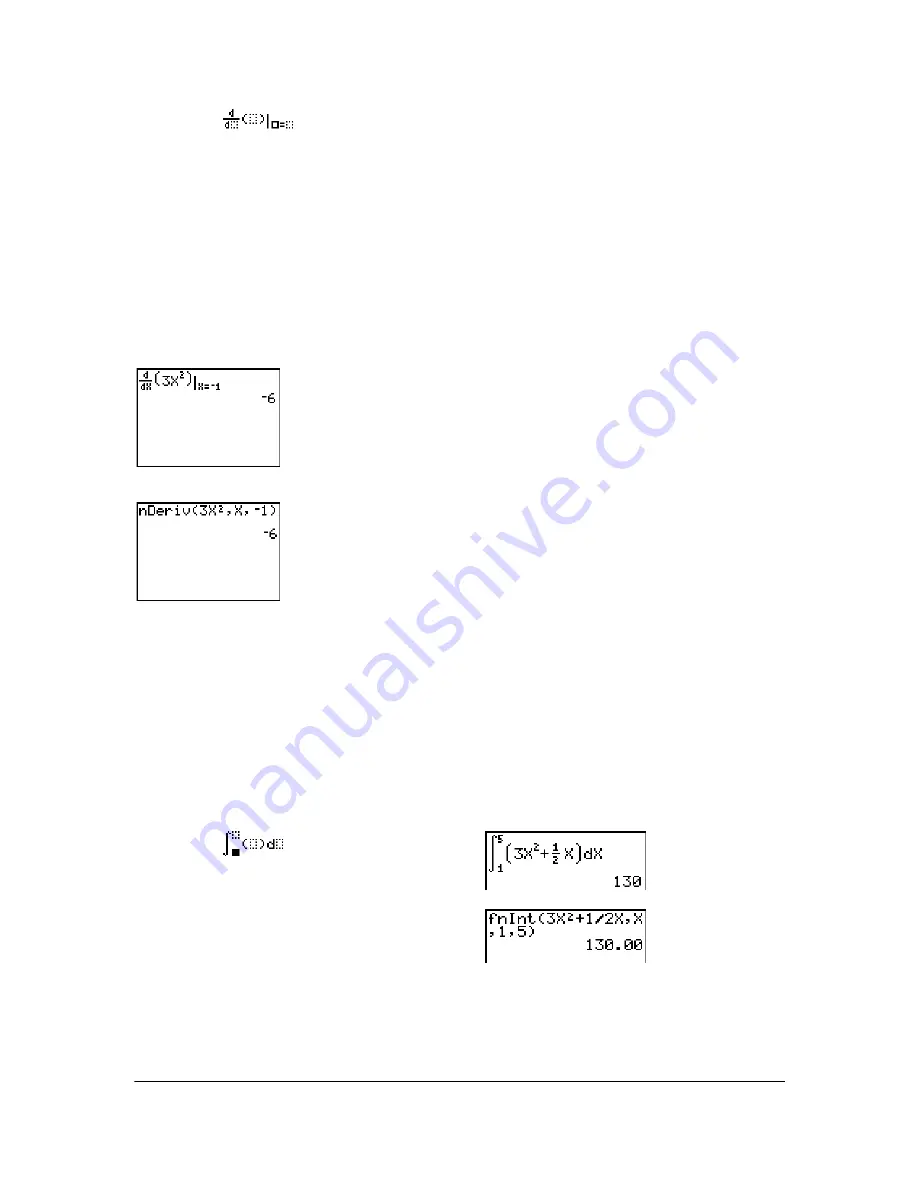
fnInt(
fnInt(
(function integral) returns the numerical integral (Gauss-Kronrod method) of
expression
with
respect to
variable
, given
lower
limit,
upper
limit, and a
tolerance
(if not specified, the default is 1
â
L
5).
fnInt(
is valid only for real numbers.
In MathPrint™ mode, the default
H
is 1
E
M
3. You can switch to Classic mode to change
H
for
investigations.
MathPrint™
Classic
MathPrint™:
Classic:
fnInt(
expression
,
variable
,
lower
,
upper
[
,
tolerance
]
)