BA 5230 en 04/2011
6.4.2.1 Fitting
•
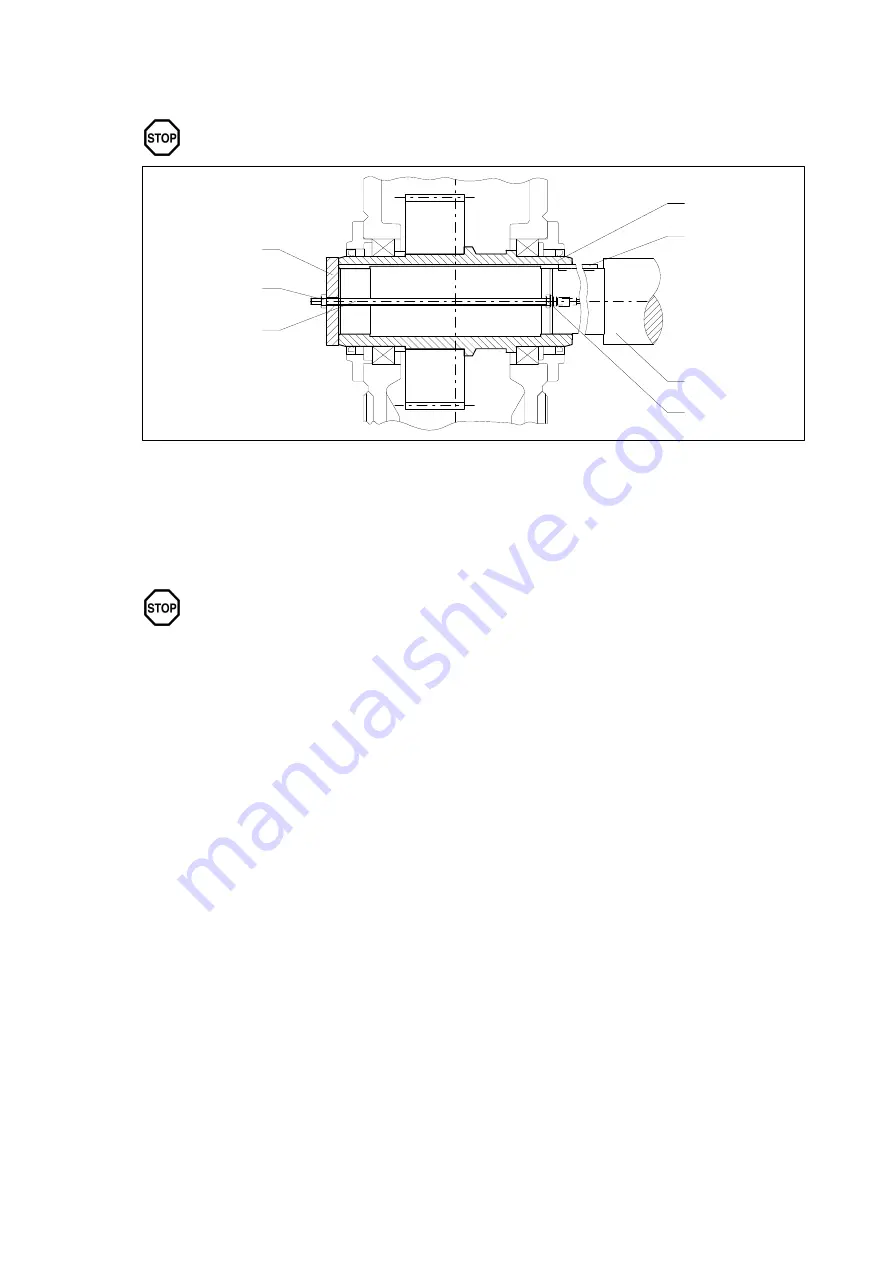
Fit the gear unit by means of nut and threaded spindle. The counterforce is provided by the hollow shaft.
The hollow shaft must be exactly aligned with the machine shaft to avoid canting.
2
3
1
4
7
6
5
Fig. 15:
Hollow shaft with parallel keyway, fitting with threaded spindle
1
Machine shaft
4
Nut
7
End plate
2
Hollow shaft
5
Threaded spindle
3
Parallel key
6
Nut
Instead of the nut and threaded spindle shown in the diagram, other types of equipment such as a hydraulic
lifting unit ("Lukas") may be used.
The hollow shaft may be tightened against a machineshaft collar only if the gearunit
configuration is one of the following:
– Torque arm
– Support with gearunit swing base
With a different arrangement the bearings may be excessively stressed.
6.4.2.2 Axial fastening
Depending on type, secure the hollow shaft axially on the machine shaft (e.g. with locking ring, end plate,
set screw).
6.4.3
Demounting
•
Remove the axial securing device from the hollow shaft.
•
If frictional corrosion has occurred on the seating surfaces, rustreleasing agent may be used in order
to facilitate forcing off the gear unit. The rust releaser can be injected through the pressureoil
connection (see figure 14), e.g. using a pump.
•
When the rustreleasing agent has taken effect, pull the gear unit off with the device (see figures 16
and 17).
•
Removing the gear unit from the drivenmachine shaft can be done, depending on local possibilities,
as follows:
─ using forcing screws in an end plate (see figure 17) or
─ using a central threaded spindle or
─ preferably using a hydraulic lifting unit ("Lukas").
















































