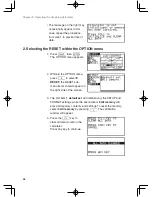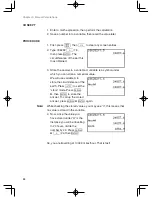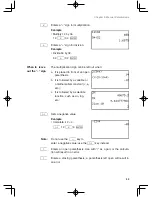
45
Chapter 2: Operating the Graphing Calculator
Precedence of Calculations
When solving a mathematical expression, this calculator internally
looks for the following figures and methods (sorted in the order of
evaluation):
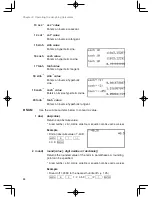
1) Fractions (1/4, a/b, , etc.)
2) Complex angles (
∠
)
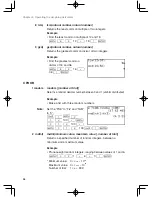
3) Single calculation functions where the numerical value occurs
before the function (X
2
, X
-1
, !, “°”, “
r
”, “
g
”, etc)
4) Exponential functions (a
b
,
a
, etc)
5) Multiplications between a value and a stored variable/constant,
with “
×
” abbreviated (2
π
, 2A, etc.)
6) Single calculation functions where the numerical value occurs
after the function (sin, cos, tan, sin
-1
, cos
-1
, tan
-1
, log, 10
x
, ln, e
x
,
√
¯, abs, int, ipart, fpart, (-), not, neg, etc.)
7) Multiplications between a number and a function in #6 (3cos20,
etc. “cos20” is evaluated first)
8) Permutations and combinations (nPr, nCr)
9)
×
,
÷
10)
+
,
–
11) and
12) or, xor xnor
13) Equalities and nonequalities (<,
≤
, >,
≥
,
≠
, =,
→
deg,
→
dms, etc.)
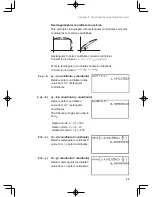
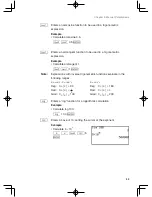
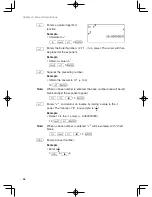
Example
The key operation and calculation precedence
5
+
2
|
s
30
+
25
|
5
a
3
E
1st
2nd
3rd
6th
5th
4th
• If parentheses are used, parenthesized calculations have
precedence over any other calculations.