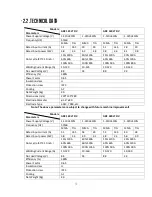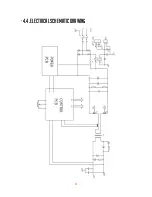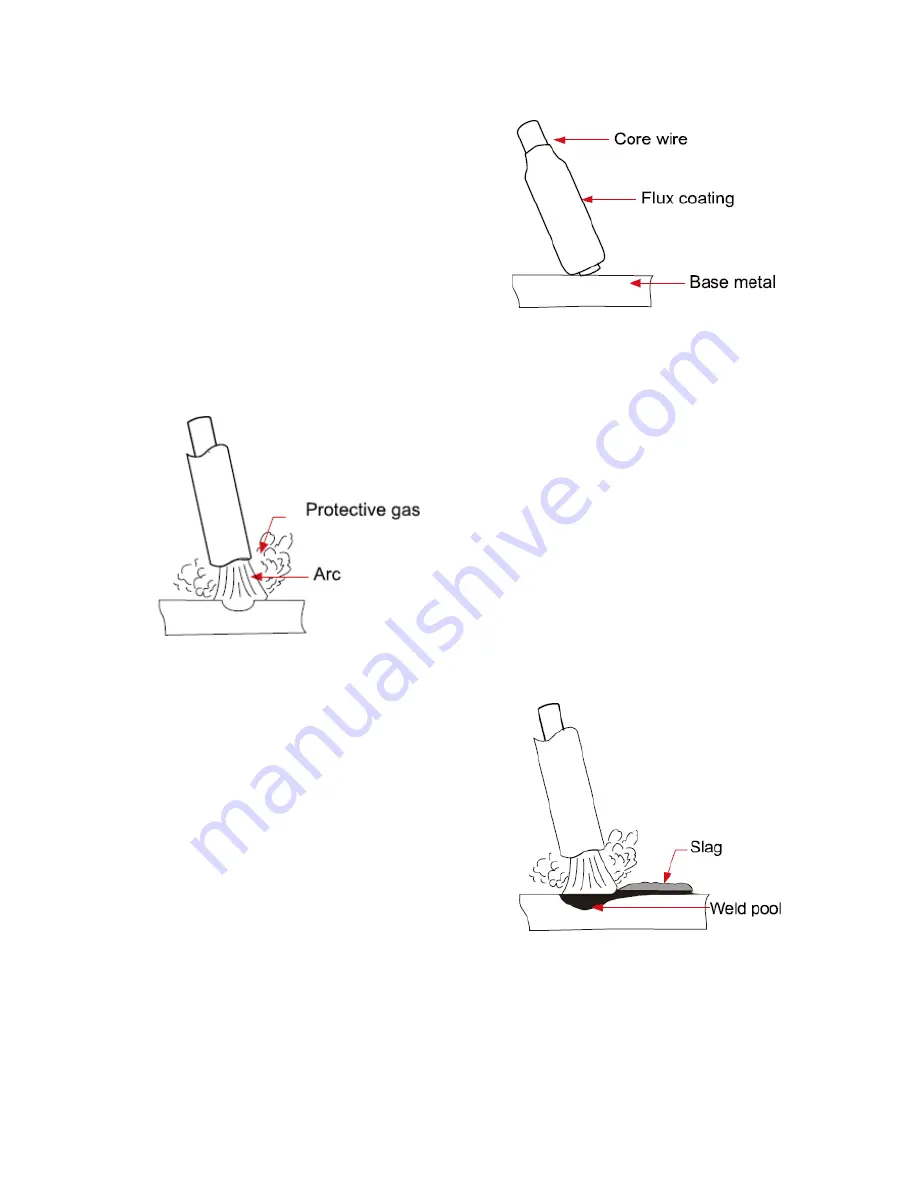
20
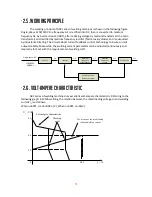
The arc is initiated by momentarily
touching the electrode to the base
metal.
The heat of the arc melts the surface of
the base metal to form a molten pool at
the end of the electrode.
The melted electrode metal is
transferred across the arc into the
molten pool and becomes the deposited
weld metal.
The deposit is covered and protected by
a slag which comes from the electrode
coating.
The arc and the immediate area are enveloped by an atmosphere of protective gas.
Manual metal arc (stick) electrodes have a solid
metal wire core and a flux coating. These electrodes
are identified by the wire diameter and by a series
of letters and numbers. The letters and numbers
identify the metal alloy and the intended use of the
electrode.
The
Metal Wire Core
works as conductor of the
current that maintains the arc. The core wire melts
and is deposited into the welding pool.
The covering on a shielded metal arc
welding electrode is called
Flux
.
The flux on the electrode performs many diferent
functions.
These include:
producing a protective gas around the
weld area
providing fluxing elements and deoxidizer
creating a protective slag coating over the
weld as it cools
establishing arc characteristics
adding alloying elements.
Covered electrodes serve many purposes in addition to filler metal tothe molten pool. These
additional functions are provided mainly by the covering on the electrode.