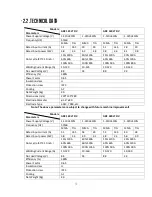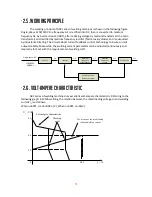
5
Never touch live electrical parts.
Wear dry, hole-free gloves and clothes to insulate your body.
Be sure to install the equipment correctly and ground the work or metal to be welded to a
good electrical (earth) ground according to the operation manual.
The electrode and work (or ground) circuits are electrically “hot” when the machine is ON.
Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare skin or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free
gloves to insulate hands.
In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode, electrode reel, welding head,
nozzle or semiautomatic welding gun are also electrically “hot”.
Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation. Make certain the insulation is
large enough to cover your full area of physical contact with work and ground.
Be Careful when using the equipment in small places, falling-off and wet circumstance.
Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical connection with the metal being
welded. The connection should be as close as possible to the area being welded.
Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and welding machine in good,
safe operating condition. Replace damaged insulation.
Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of electrode holders connected to two
welders because voltage between the two can be the total of the open circuit voltage of
both welders.
When working above the floor level, use a safety belt to protect yourself from a fall should
you get an electric shock!
FUMES AND GASES CAN BE DANGEROUS.
Smoke and gas generated whilst welding or cutting can be harmful to people’s health. Welding
produces fumes and gases. Breathing these fumes and gases can be hazardous to your health.
Do not breathe the smoke and gas generated whilst welding or cutting, keep your head
out of the fumes. Use enough ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep fumes and
gases away from the breathing zone. When welding with electrodes which require special
ventilation such as stainless or hard facing or on lead or cadmium plated steel and other
metals or coatings which produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as low as possible and
below the Threshold Limit Values using local exhaust or mechanical ventilation. In
confined spaces or in some circumstances, outdoors, a respirator may be required.
Additional precautions are also required when welding on galvanized steel.
Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon vapors coming from degreasing,
cleaning or spraying operations. The heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors
to form phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating products.
Shielded gases used for arc welding can displace air and cause injury or death. Always use
enough ventilation, especially in confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.