NEC SL1100
Issue 6.0
Networking Manual
9 - 41
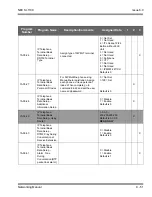
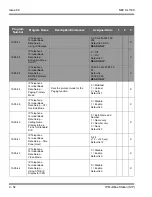
RTP Header Compression
compacts the RTP header from 40 bytes in size
to 2 ~ 4 Bytes in size. RTP header compression is used only on low speed
links. Regularly on every voice packet there is an IP/UDP/RTP header that is
40 bytes in length. Compressing this header, down to 2 ~ 4 bytes, can save a
considerable amount of bandwidth. The following is an example of a VoIP
packet without RTP header compression and one of a packet with RTP
header compression.
Notice that the overall packet size, when using RTP header compression, is
considerably smaller.
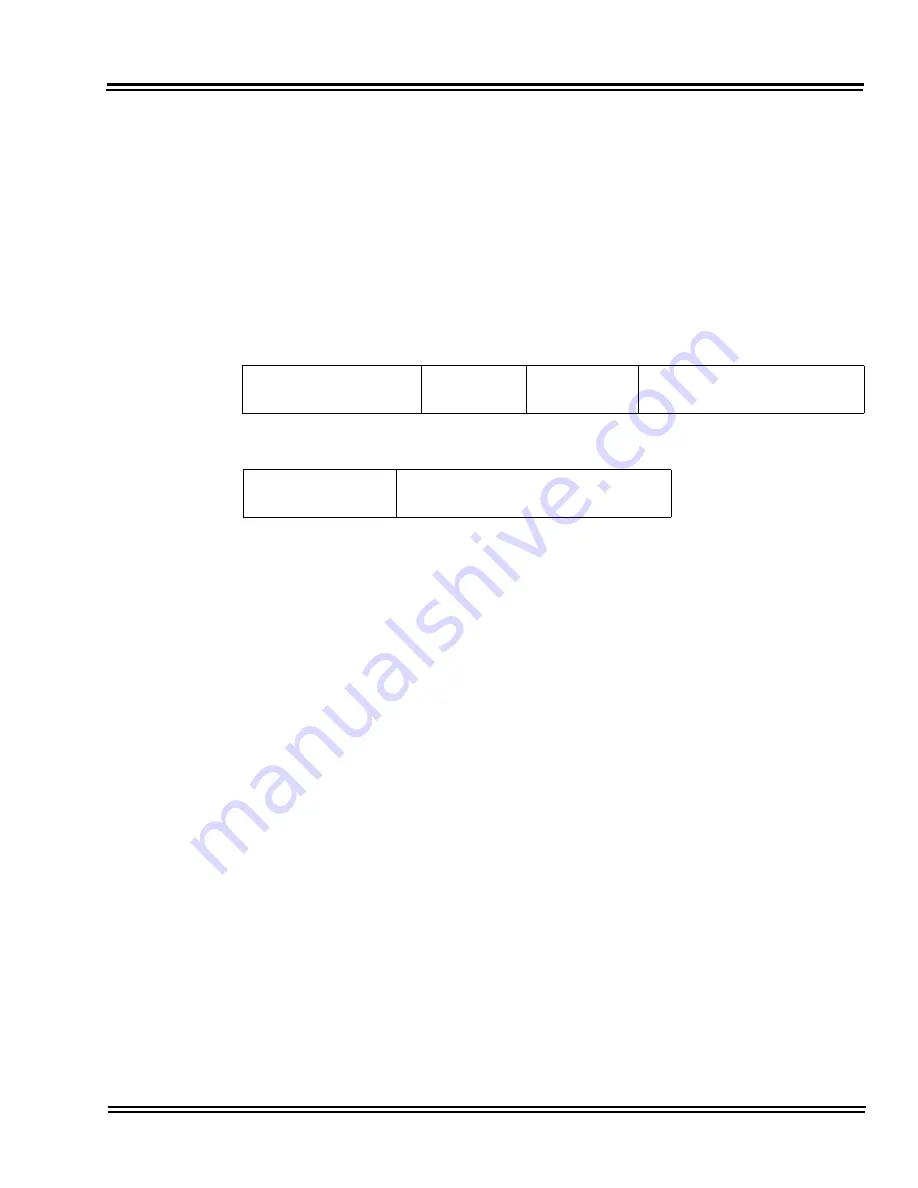
VoIP packet without RTP header compression
VoIP packet with RTP header compression
Voice Activity Detection
(VAD) is suppression of silence packets from being
sent across the network. In a VoIP network all conversations are packetized
and sent, including silence. On an average a typical conversation contain
anywhere from 35% ~ 45% silence. This can be interrupted as 35% ~ 45%
transmission of VoIP packets, as having no audio, using valuable bandwidth.
With the VAD option enabled, the transmitting of packets stops after a
threshold is met determining silence. The receiving side then injects comfort
noise into the call so it does not appear the call has dropped.
Bandwidth Calculations
The first step in calculating the bandwidth of a call is determining how many
bytes the voice payload is going to use. The amount is directly affected by the
CODEC and packet size. Below are the supported default CODEC speeds for
SIP Multiline telephones.
G.711 = 64000bps
G.722 = 64000bps
G.729 = 8000bps
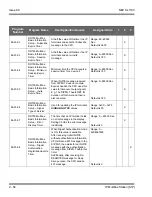
Payload Calculation Voice
(Packet size * CODEC bandwidth) / 8 = Voice Payload in Bytes
Example of G.711 with a 20ms packet size
IP Header
20 bytes
UDP Header
8 Bytes
RTP Header
12 bytes
VOICE PAYLOAD
Compressed
Header 2 ~ 4 bytes
VOICE PAYLOAD
Summary of Contents for SL1100
Page 1: ...Networking Manual NDA 31190 Issue 6 0 SL1100...
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 22: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 1 2 Introduction THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 62: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 5 30 Programming THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 94: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 6 32 Network Design Considerations THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 134: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 8 10 DHCP Client THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
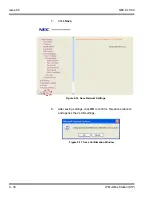
Page 159: ...NEC SL1100 Issue 6 0 Networking Manual 9 25 Figure 9 7 Log In to IP Phone...
Page 181: ...NEC SL1100 Issue 6 0 Networking Manual 9 47 Figure 9 25 IP System Operation Setup...
Page 206: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 9 72 IP Multiline Station SIP Figure 9 36 NAPT Configuration Example...
Page 230: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 10 18 IP Single Line Telephone THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 232: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 11 2 NAPT Figure 11 1 NAPT Configuration Example...
Page 242: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 12 4 All DSP Busy Indication THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 290: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 13 48 SL Net THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 291: ......
Page 292: ...SL1100 Networking Manual NEC Corporation of America Issue 6 0...