NEC SL1100
Issue 6.0
Networking Manual
9 - 19
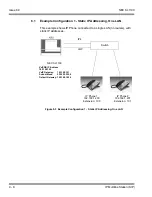
The cabling infrastructure can be simplified. There is no longer a need
for separate cabling for the phone system. Built into the IP phones is a 2
port 10/100 manageable data switch. The data connection for the PC is
available on the back of the IP phone. This built in data switch also
supports 802.1Q and 802.1 P VLAN tagging abilities. The data and the
voice can be tagged separately.
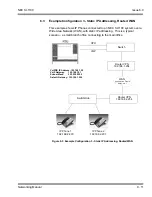
Allows you to connect remote office workers with a telephone that has
the look and same functionality as the telephones connected at the
office.
SIP is used for VoIP as defined by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
RFC3261. The NEC SIP MLT uses IP Multiline Station (SIP) (proprietary
enhanced SIP protocol) to facilitate the multifunction, multiline telephone.
The SIP Multiline Telephone interfaces directly to the CPU that houses the
VoIPDB daughter board. The VoIPDB provides the digital signal processors
(DSPs) for IP stations and trunks.
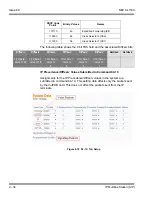
VoIPDB provides 32 DSPs
A DSP provides format conversion from circuit switched networks (TDM) to
packet switched networks (IP). Each voice channel from the circuit switched
network is compressed and packetized for transmission over the packet
network. In the reverse direction, each packet is buffered for de-jittering,
decompressed and sent to the circuit switched network. Each DSP converts a
single speech channel from IP to TDM and vice versa.
The following are examples of DSP allocation.
Calling from an IP phone to a TDM phone uses one DSP.
Calling from an IP phone to another IP phone, registered to the same
CPU, uses no DSPs.
Calling from a TDM phone to another TDM phone uses no DSPs.
Calling from a TDM phone and out an IP trunk uses one DSP.
An IP to IP call is peer-to-peer, and no DSP resource is used. When this
feature is deactivated, an IP to IP call consumes two DSP resources.
Summary of Contents for SL1100
Page 1: ...Networking Manual NDA 31190 Issue 6 0 SL1100...
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 22: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 1 2 Introduction THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 62: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 5 30 Programming THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 94: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 6 32 Network Design Considerations THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 134: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 8 10 DHCP Client THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
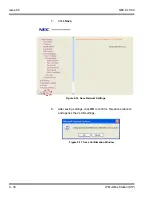
Page 159: ...NEC SL1100 Issue 6 0 Networking Manual 9 25 Figure 9 7 Log In to IP Phone...
Page 181: ...NEC SL1100 Issue 6 0 Networking Manual 9 47 Figure 9 25 IP System Operation Setup...
Page 206: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 9 72 IP Multiline Station SIP Figure 9 36 NAPT Configuration Example...
Page 230: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 10 18 IP Single Line Telephone THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 232: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 11 2 NAPT Figure 11 1 NAPT Configuration Example...
Page 242: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 12 4 All DSP Busy Indication THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 290: ...Issue 6 0 NEC SL1100 13 48 SL Net THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK...
Page 291: ......
Page 292: ...SL1100 Networking Manual NEC Corporation of America Issue 6 0...