19
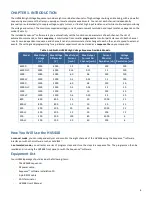
Channel Output Limits
To protect external equipment, you can set hard limits for the current and voltage on each channel. Enter lower and upper
Output limits for voltage and/or current.
These limits are particularly useful in automated mode, to ensure that the output voltage/current stays within bounds regardless
of instructions from the sequence. If an out-of-bounds condition occurs, the channel will trip (i.e., will float to the controlling
voltage) or clip (i.e., will be forced within the limit values), depending on the channel’s trip-handling settings (see
Error
Reporting/Trip Settings
) below.
Note
:
The HVS448 has an overall maximum output current (value depends on the model, see
Table 1
). If the total of the
current settings across all channels exceeds this maximum, the overload circuit will trip, and the outputs will
temporarily become inputs (i.e., they float to the driving voltage).
Holdoff
value is the duration that the channel must stay beyond the voltage/current limits for the trip settings to take effect.
Error Reporting/Trip Settings
The HVS448 channels continuously check the validity of their settings. In response to invalid conditions, the channels can trip,
clip, or ignore different types of errors. Each channel can have different settings. If Monitoring is turned on for a channel, any
problems on that channel will cause a message to appear in the
Errors
field.
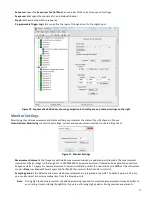
Click the
Trip Setting
button to choose the error responses for a channel. The
Becomes an Input on
dialog box will be displayed
(see
Figure 13
).
Figure 13. Channel Error Handling Dialog Box
Table 3
describes error messages that may be observed while using the Sequence software.
Table 3. Error Descriptions
Error
Meaning
If box is checked
If box is not
checked
Error Message
Numerical
Exception
Overflow/underflow in a
mathematical calculation (e.g., square
root of a negative number attempted)
Channel becomes an
input (i.e., floats to
driving voltage)
Error is
ignored
“A numerical exception
occurred.”
Current at limit The current exceeds the channel
limits
Channel becomes an
input
Clip to current
limit
“The current exceeded
the limits.”
Voltage at limit The voltage exceeds the channel
limits
Channel becomes an
Input
Clip to voltage
limit
“The voltage exceeded
the limits.”
Mismatched
units in
calculations
A mathematical operation was
attempted on numbers with
incompatible units (e.g., voltage
added to time)
Channel becomes an
input
Error is
ignored
“Calculations were
performed on numbers
having inconsistent
units.”
Output setting
beyond limits
The output of the power supply is
exceeded
Channel becomes an
input
Clip to current
or voltage
limit
“The supply was
instructed to regulate
beyond its prescribed
limits.”