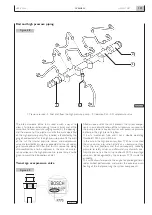
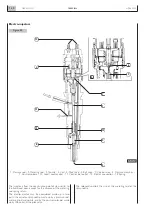
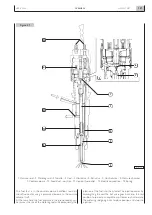
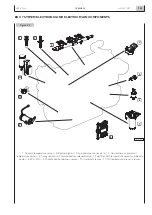
Pre-injection
By this term it is stated the delivery of a limited amount of fuel
that is obtained in the short interval of opening and closing of
the spray-nozzle metering rod, before the main injection.
Pre-injection is programmed in the ECU and it is possible up
to 2,000 RPM. Its purpose is to limit the pressure increase
gradient within the combustion chamber to reduce its peaks
and contain typical noise of the direct injection engines.
The amount of fuel injected is an integral part of main
metered injection.
Injection pressure modulation
The best and more reliable torque and power delivery, com-
plying with fumes and acoustic emission containment,is made
possible, by having a high pressure fuel delivery and by using
injectors having a high atomization. In order to adequate fuel
metering with the high dynamics required by the engine con-
trol,as well as managining the injection time it is also neces-
sary managing the pressure of the fuel injected.
This goal is obtained in loop by using the datum supplied by
the pressure sensor located on the time sharing apparatus.
Idling adjusting
This function enables to obtain a constant and repeatable
RPM notwithstanding the changing of the operational envi-
ronmental conditions.The adjustment is obtained by manag-
ing metering and the injection beginning instant according to
the processing of the information produced by the sensors.
If accumulator voltage is below efficiency rating, ECU increas-
es rotation to improve alternator recharging.
Selfdiagnosis
It is the constant check of the presence of the electrical sig-
nals sent by the sensors or delivered to actuators. In the case
of anomalies being detected it enables the electronic unit to
process data according to a “recovery” programme.
The central unit, not only checks the efficiency of the sensors,
actuators and wiring connected to them but it also checks a
consistency evaluation of the signals and the information
deducted from them.
It is possible to recognise an inconsistency and not use an
invalidated datum replacing it with that one predefined by
means of comparison with pre-programmed limit parame-
ters or by assessing their increasing or decreasing gradient.
The “recovery” procedure is integrated by the storing of the
codes identifying the errors detected. These codes can be
decoded by using diagnostic computerized appliances or by
means of tell tale light blinking named “blink code”.
Functions stated here below are actuated only under special
engine operation conditions:
EDC indicator light
It is located on the instrument and control panel, it is direct-
ly controlled by EDC system from the central unit. It is nor-
mally off, it will come on for an instant immediately after hav-
ing supplied the system by means of an efficiency test.
If lit, EDC indicator states a likely anomaly of the injection sys-
tem or an irregular engine operation or of one of its machine
members.
Fuel Heating
It assures a correct density of the fuel even at low tempera-
tures, improving atomization in order to obtain a better gra-
dient smoke and emissions.
The heating elements is actuated on the filter according to
the temperature detected.
Linearization of the acceleration gradient
The exhaust and acoustic noxious emissions containment
has been obtained by implementing strategies especially to
control injections required by accelerations. Management of
the fuel metering and advance, during transient states,has
been obtained by devising experimental progression ways
stored in the central unit.
Balance of the cylinder torque delivery
It contributes to reduce vibrations and equilibrates its
operation.
It is obtained by controlling delivery and injection advance
“cylinder by cylinder”; in such a way it is possible to adequate
crankshaft angular acceleration produced by each combus-
tion to equal ratings.
Cylinders balance can be carried out only at idle speed, due
to software structure complexity, but data thus gathered
with a wise adaptation, can be used for higher speed too.
Rotation speed control
It represents the electronic equivalent of the speed controls
of the traditional injection pumps.
Like the latters it has the following adjustment characteristics:
-
Minum and maximum
-
Every speed
Top speed limitation
It preserves the efficiency of the engine operation by not
allowing runaway speed even if accidental.
Limitation strategies are actuated in the following ways:
-
When the first threshold is overcome,fuel delivery
reduces progressively.
-
When the top speed foreseen has been reached fuel
delivery is zeroed.
Cut off
It consists in non injecting fuel during the engine deceleration
phase. The function is operating until the idle speed is
reached below which it would be impossible to restore
engine thermic operation.
De rating
It can be considered as a recovery programme. It does not
produces a storage of an anomaly record. It is caused by
the recognition of fuel high temperature, or coolant or
comburent air. De rating consists in reducing the torque
delivered by the engine to presere it from operation ineffi-
ciency. It actuates by overcoming pre set thresholds, in a
way proportional and gradual to the amount of the over-
coming of parameter; it does not entail fault signalling on
the instrument panel.
N60 ENT M37
OVERVIEW
1.50
APRIL 2004
Summary of Contents for N60 ENT M37
Page 4: ...N60 ENT M37 IV APRIL 2004 ...
Page 52: ...N60 ENT M37 OVERVIEW 1 52 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 54: ...N60 ENT M37 TECHNICAL DATA 2 54 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 60: ...N60 ENT M37 TECHNICAL DATA 2 60 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 62: ...N60 ENT M37 ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT 3 62 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 92: ...N60 ENT M37 DIAGNOSTICS 4 92 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 116: ...N60 ENT M37 DIAGNOSTICS 4 116 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 118: ...N60 ENT M37 MAINTENANCE 5 118 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 122: ...N60 ENT M37 MAINTENANCE 5 122 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 124: ...N60 ENT M37 SERVICING OPERATIONS ON INSTALLED ENGINE 6 124 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 139: ...SECTION 7 TOOLS Page TOOLS 141 N60 ENT M37 TOOLS 7 139 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 140: ...N60 ENT M37 TOOLS 7 140 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 146: ...N60 ENT M37 TOOLS 7 146 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 156: ...APRIL 2004 OVERHAUL 8 156 N60 ENT M37 ...
Page 164: ...APRIL 2004 OVERHAUL 8 164 N60 ENT M37 ...
Page 181: ...OVERHAUL APRIL 2004 N60 ENT M37 8 181 ...
Page 188: ...N60 ENT M37 OVERHAUL 8 188 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 190: ...N60 ENT M37 SAFETY PRESCRIPTIONS 9 190 APRIL 2004 ...
Page 193: ......