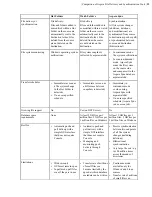
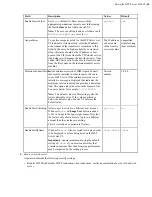
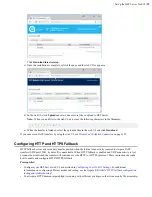
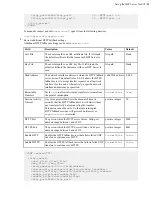
| Installation and Upgrades |
18
Depending on your
sshd_config
file, you might have additional instances of
AllowTCPForwarding
that
are set to the default
Yes
. Review your
sshd_config
file for other instances and disable if necessary.
Disabling TCP forwarding does not improve security unless users are also denied shell access, because they can
still install their own forwarders. Review your user and file permissions, and see
page 33 for instructions on modifying user shell access.
4.
Update authentication methods
Public key authentication can prevent brute-force SSH attacks if all password-based authentication methods are
disabled. For this reason, Aspera recommends disabling password authentication in the
sshd_config
file and
enabling private/public key authentication.
Note:
Before proceeding, configure at least one non-root, non-transfer user with a public key to use to manage the
server. This is because in other server-securing steps, root login is disabled and Aspera recommends that transfer
users are restricted to aspshell, which does not allow interactive login. This user and public key is what you use to
access and manage the server as an administrator.
To configure authentication methods, add or uncomment
PubkeyAuthentication yes
and comment out
PasswordAuthentication yes
.
PubkeyAuthentication yes
#PasswordAuthentication yes
PasswordAuthentication no
Note:
If you choose to leave password authentication enabled, be sure to advise account creators to use strong
passwords and set
PermitEmptyPasswords
to "no".
PermitEmptyPasswords no
5.
Disable root login.
CAUTION:
This step disables root access. Make sure that you have at least one user account with sudo
privileges before continuing, otherwise you may not have access to administer your server.
By default, OpenSSH allows root logins. However, disabling root access helps maintain a more secure server.
Aspera recommends disabling root access by commenting out
PermitRootLogin yes
in the
sshd_config
file and adding
PermitRootLogin No
.
#PermitRootLogin yes
PermitRootLogin no
Administrators can use the
su
command when root privileges are necessary.
6.
Restart the SSH server to apply new settings.
Restarting your SSH server does not affect currently connected users
.
# systemctl restart sshd.service
or for Linux systems that use
init.d
:
# service sshd restart
7.
Review your logs periodically for attacks.
You can view the state of active TCP connections by running the
netstat
command:
# netstat -an
Typical output shows multiple, different IP addresses connected to specific ports:
TCP 10.0.111.200:53402 72.21.81.109:80 CLOSE_WAIT