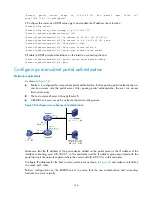
136
With the portal server detection function, the router (access device) can detect the status of a specific
portal server. The specific configurations include the following:
1.
Detection methods (choose either or both):
{
Probing HTTP connections
—The access device periodically sends TCP connection requests to the
HTTP service port of the portal servers configured on its interfaces. If the TCP connection with a
portal server can be established, the access device considers that the probe succeeds (the HTTP
service of the portal server is open and the portal server is reachable). If the TCP connection
cannot be established, the access device considers that the probe fails and that the portal server
is unreachable.
{
Probing portal heartbeat packets
—A portal server that supports the portal heartbeat function
(only the portal server of iMC supports this function) sends portal heartbeat packets to portal
access devices periodically. If an access device receives a portal heartbeat packet or an
authentication packet within a probe interval, the access device considers that the probe
succeeds and that the portal server is reachable. Otherwise, it considers that the probe fails
and that the portal server is unreachable.
2.
Probe parameters:
{
Probe interval
—Interval at which probe attempts are made.
{
Maximum number of probe attempts
—Maximum number of consecutive probe attempts
allowed. If the number of consecutive probes reaches this value, the access device considers
that the portal server is unreachable.
3.
Actions to be taken when the server reachability status changes (choose one or more):
{
Sending a trap message
—When the status of a portal server changes, the access device sends
a trap message to the NMS. The trap message contains the portal server name and the current
state of the portal server.
{
Sending a log
—When the status of a portal server changes, the access device sends a log
message. The log message indicates the portal server name and the current state and original
state of the portal server.
{
Disabling portal authentication and enabling portal authentication bypass
—When the access
device detects that a portal server is unreachable, it disables portal authentication on the
interfaces that use the portal server (allows all portal users on the interfaces to access network
resources). When the access device receives from the portal server portal heartbeat packets or
authentication packets (such as logon requests and logout requests), it re-enables the portal
authentication function.
Configure any combination of the described configuration items as needed:
•
If both detection methods are specified, a portal server is regarded as unreachable as long as one
detection method fails, and an unreachable portal server is regarded as recovered only when both
detection methods succeed.
•
If multiple actions are specified, the access device executes all the specified actions when the status
of a portal server changes.
•
The detection function configured for a portal server takes effect on an interface only after you
enable portal authentication and reference the portal server on the interface.