317
# Enable the SSH server.
[Router] ssh server enable
# Configure an IP address for interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, which the SSH client uses as the
destination for SSH connection.
[Router] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.40 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Set the authentication mode for the user interfaces to AAA.
[Router] user-interface vty 0 4
[Router-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode scheme
# Enable the user interfaces to support SSH.
[Router-ui-vty0-4] protocol inbound ssh
[Router-ui-vty0-4] quit
# Create local user
client001
, and set the user command privilege level to 3.
[Router] local-user client001
[Router-luser-client001] password simple aabbcc
[Router-luser-client001] service-type ssh
[Router-luser-client001] authorization-attribute level 3
[Router-luser-client001] quit
# Specify the service type for user
client001
as
Stelnet
and the authentication method as
password
. This
step is optional.
[Router] ssh user client001 service-type stelnet authentication-type password
2.
Establish a connection between the SSH client and SSH server.
NOTE:
The router supports a variety of SSH client software, such as PuTTY and OpenSSH. The following is an
example of configuring an SSH client that uses PuTTY Version 0.58.
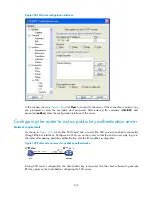
# Establish a connection to the SSH server.
Launch PuTTY.exe to enter the following interface. In the
Host Name (or IP address)
text box, enter the IP
address of the server.