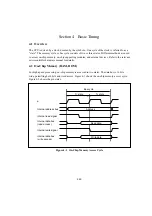
Section 3 Processing States
3.1 Overview
The CPU has five main processing states: the program execution state, exception handling state,
power-down state, reset state, and bus-released state. The power-down state includes sleep mode,
software standby mode, and hardware standby mode. Figure 3-1 shows a diagram of the
processing states. Figure 3-2 indicates the state transitions. For details, refer to the relevant
microcontroller hardware manual.
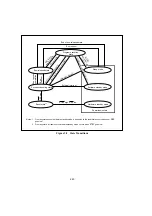
Figure 3-1 Processing States
Program execution
state
The CPU executes program instructions in sequence.
Exception-handling
state
A transient state in which the CPU executes a hardware
sequence (saving the program counter and condition-code
register, fetching a vector, etc.) in response to a reset,
interrupt, or other exception.
Bus-released state
The external bus has been released in response to an external
or internal bus request signal.
Reset state
The CPU and all on-chip supporting modules have been
initialized and are stopped.
Power-down state
Some or all clock signals are
stopped to conserve power.
Sleep mode
Software standby
mode
Hardware standby
mode
Processing
states
239