7
Subject to change without notice
Type of signal voltage
With the HM304, most repetitive
signals in the frequency
range up to at least 35MHz (-3dB)
can be examined.
Sinewave signals of 50MHz are displayed with a height of
approx. 50% (-6dB). However when examining square or
pulse type waveforms, attention must be paid to the harmonic
content of such signals. The repetition frequency (fundamen-
tal frequency) of the signal must therefore be significantly
smaller than the upper limit frequency of the vertical amplifier.
Displaying composite signals can be difficult, especially if they
contain no repetitive higher amplitude content which can be
used for triggering. This is the case with bursts, for instance.
To obtain a well-triggered display in this case, the assistance
of the variable holdoff and/or delay function may be required.
Television video signals are relatively easy to trigger using
the built-in TV-Sync-Separator (TV).
For optional operation as a DC or AC voltage amplifier, the
vertical amplifier input is provided with a DC/AC switch. The
DC position should only be used with a series-connected
attenuator probe or at very low frequencies or if the
measurement of the DC voltage content of the signal is
absolutely necessary.
When displaying very low frequency pulses, the flat tops may
be sloping with AC coupling of the vertical amplifier (AC limit
frequency approx. 1.6 Hz for 3dB). In this case, DC operation
is preferred, provided the signal voltage is not superimposed
on a too high DC level. Otherwise a capacitor of adequate
capacitance must be connected to the input of the vertical
amplifier with DC coupling. This capacitor must have a
sufficiently high breakdown voltage rating. DC coupling is
also recommended for the display of logic and pulse signals,
especially if the pulse duty factor changes constantly.
Otherwise the display will move upwards or downwards at
each change. Pure direct voltages can only be measured with
DC-coupling.
Amplitude Measurements
In general electrical engineering, alternating voltage data
normally refers to effective values (rms = root-mean-square
value). However, for signal magnitudes and voltage
designations in oscilloscope measurements, the peak-to-peak
voltage (Vpp) value is applied. The latter corresponds to the
real potential difference between the most positive and most
negative points of a signal waveform.
If a sinusoidal waveform, displayed on the oscilloscope
screen, is to be converted into an effective (rms) value, the
resulting peak-to-peak value must be divided by 2x
√
2 = 2.83.
Conversely, it should be observed that sinusoidal voltages
indicated in Vrms (Veff) have 2.83 times the potential
difference in Vpp. The relationship between the different
voltage magnitudes can be seen from the following figure.
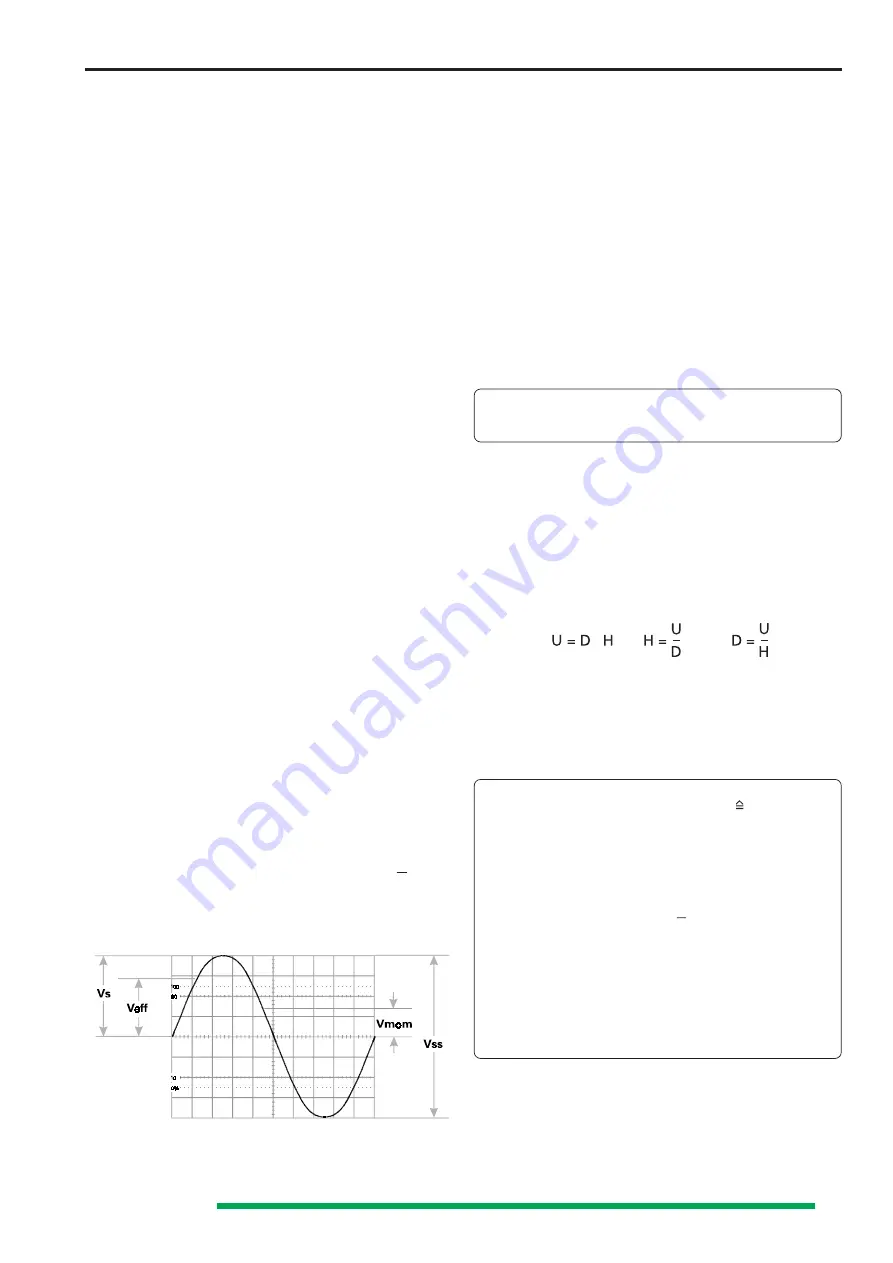
Voltage values of a sine curve
Vrms = effective value; Vp = simple peak or crest value;
Vpp = peak-to-peak value; Vmom = momentary value.
The minimum signal voltage which must be applied to the Y
input for a trace of 1div. height is 1mVpp when the 1mV LED
is lit and the vernier is set to CAL by turning the fine
adjustment knob within the VOLTS/DIV. section fully
clockwise. However, smaller signals than this may also be
displayed. The deflection coefficients on the input attenuators
are indicated in mV/div. or V/div. (peak-to-peak value).
The magnitude of the applied voltage is ascertained by
multiplying the selected deflection coefficient by the vertical
display height in div. If an attenuator probe x10 is used, a
further multiplication by a factor of 10 is required to ascertain
the correct voltage value.
For exact amplitude measurements, the variable control
( VAR. 2.5:1) must be set to its calibrated detent CAL
position.
When turning the variable control ccw, the
deflection coefficient LED will start to blink and the sensitivity
will be reduced until a maximum factor of 2.5 is reached.
Therefore any intermediate value is possible within the 1-2-5
sequence.
With direct connection to the vertical input, signals
up to 400Vpp may be displayed (attenuator set to 20V/
div., variable control to left stop).
With the designations
H
= display height in div.,
U
= signal voltage in Vpp at the vertical input,
D
= deflection coefficient in V/div. at attenuator switch,
the required value can be calculated from the two given
quantities:
However, these three values are not freely selectable. They
have to be within the following limits (trigger threshold,
accuracy of reading):
H
between 0.5 and 8div., if possible 3.2 to 8div.,
U
between 1mVpp and 160Vpp,
D
between 1mV/div. and 20V/div. in 1-2-5 sequence.
Examples:
Set deflection coefficient
D
= 50mV/div. 0.05V/div.,
observed display height
H
= 4.6div.,
required voltage
U
= 0.05x4.6 = 0.23Vpp.
Input voltage
U
= 5Vpp,
set deflection coefficient
D
= 1V/div.,
required display height
H
= 5:1 = 5div.
Signal voltage
U
= 230Vrmsx2
√
2 = 651Vpp
(voltage > 160Vpp, with probe 10:1:
U
= 65.1Vpp),
desired display height
H
= min. 3.2div., max. 8div.,
max. deflection coefficient
D
= 65.1:3.2 = 20.3V/div.,
min. deflection coefficient
D
= 65.1:8 = 8.1V/div.,
adjusted deflection coefficient
D
= 10V/div.
The input voltage must not exceed 400V, independent
from the polarity.
If an AC voltage which is superimposed on a DC voltage is
applied, the maximum peak value of both voltages must not
or -400V. So for AC voltages with a mean value of
zero volt the maximum peak to peak value is 800Vpp.
If attenuator probes with higher limits are used, the
probes limits are valid only if the oscilloscope is set to
⋅






















