F R O N T C O N S O L E
C H A P T E R 3
The selected filter is displayed as an overlay to help the user visualize the filter. Shown are the
main RX filter (green, VFO-A), the MultiRX filter (blue, VFO-B) and the TX filter edges (yellow
vertical lines). The color of all the filter overlays can be changed independently using the Setup
Form-Appearance Tab, Display Sub-Tab (page 116).
The frequency scale shows the actual frequency (in MHz).
The edges of the amateur bands are marked as red vertical lines and the corresponding
frequencies are displayed in red
With the mouse, filters and filter edges can be varied by dragging and dropping
Point click tuning is available with mouse and cross hairs showing.
The Panadapter is useful because although you hear only the signals within the audio passband, you
can see in real time all signals within the receiver’s passband (as determined by the sampling rate).
This gives a much more complete picture of the surrounding area in the band, especially when there is
abundant signal activity (e.g. contest and DX situations).
Histogram
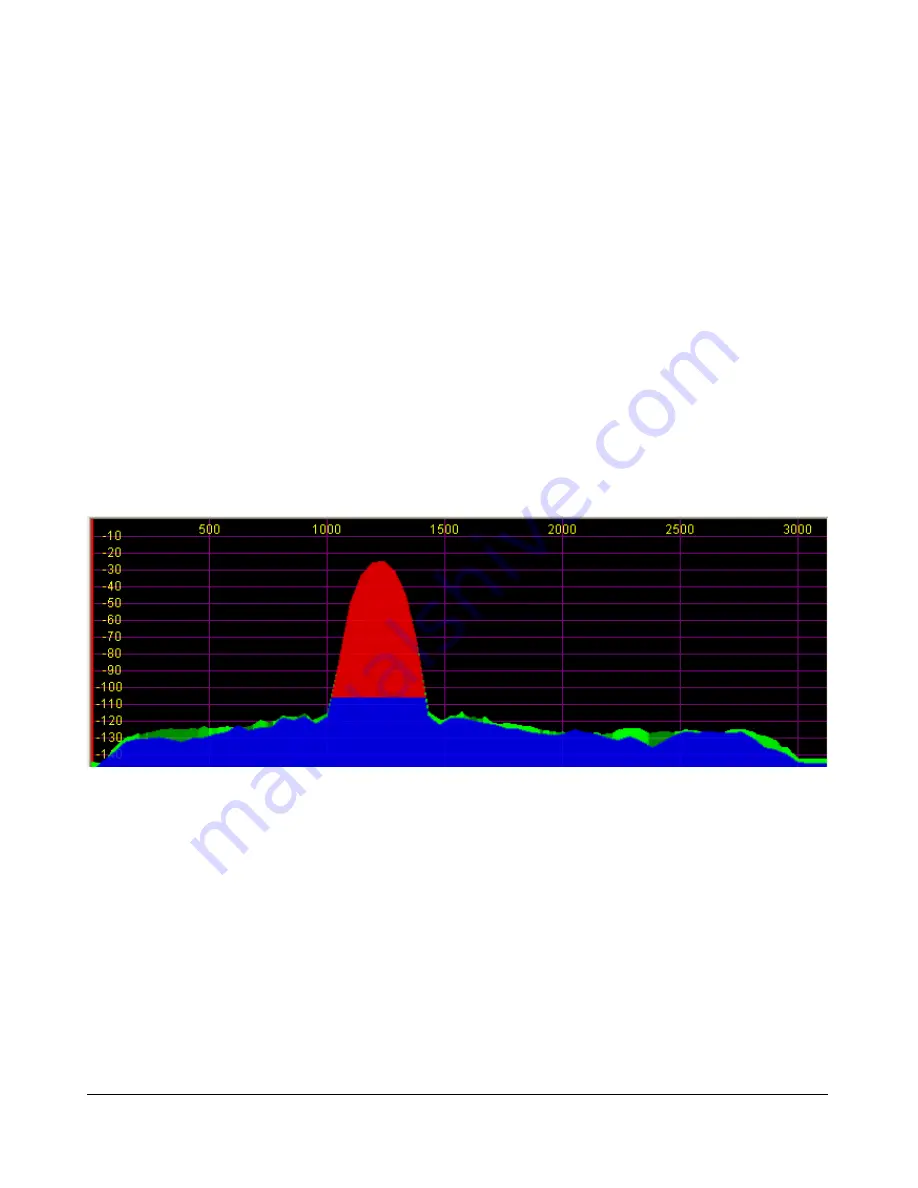
Figure 49: Histogram Display Mode
The Histogram Display is similar to the Spectrum Display, but instead of a single color data line,
additional colored data is used. Blue signals are real-time (current) signals that are below a signal
threshold (roughly below the average plus a small margin). The red signals are real-time (current)
signals that are above that same threshold. The green signals are previous peaks on that same
frequency that will fade as time goes by (a type of history, hence the name).
[The rest of this page has been left blank intentionally]
65
2003-2008 FlexRadio Systems
















































