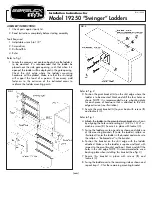
2. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
Page 21
© 2005 - 2007 DH Instruments, a Fluke Company
2.2.1.5
AMH-38 MASS SET
The masses of the 38 kg mass set are loaded onto in the piston-cylinder as required
to apply a force corresponding the the set pressure desired. The AMH-38 mass
handler (see Section 2.2.1.4) loads and unloads the masses automatically.
Figure 18.
AMH-38 mass set
2.2.2
FPG8601 FORCE BALANCED PISTON GAUGE
The ADCS-601-AF Air Data Calibration Standard includes an FPG8601 force balanced
piston gauge to cover the air data pressure range below the range of the PG7601 gas
operated piston gauge. The FPG8601 system includes:
-
FPG8601 piston gauge platform with terminal and 10 kPa/kg piston-cylinder (installed
on Reference Bench).
-
Capacitance diaphragm gauge with display and isolation valve for measurement of
FPG8601 reference vacuum in absolute mode (mounted on platform).
-
PPC3-100K A116Ks/BG15Ks, pressure controller to automate FPG8601 system
pressure control (see Section 2.2.3) (in control cabinet).
-
MS-8601-2, 2 kg mass set with hanger for validation of FPG8601 load cell linearity.
(accessory used separately in metrological maintenance (see Section 7.2.5)).
The FPG8601 force balanced piston gauge and PPC3 pressure controller are stand alone
products for which separate Operation and Maintenance manuals are available with much
more complete information than is included in this manual. A copy of the FPG8601
manual is provided on the ADCS-601-AF Support CD and is available at
www.dhinstruments.com.
The FPG8601 operates on the principle of the piston gauge (see Section 2.2.1); however, the
force resulting from a difference in pressure across the piston is measured by a force
balanced, load cell rather than balanced directly against masses subjected to the
acceleration due to gravity (see Figure 11). The piston-cylinder is suspended from the load
cell. Rather than rotating the piston in the cylinder, the piston-cylinder gap is conical and gas
flow through the gap is used to center the piston. The force across the piston is transmitted
to the load cell through a coupling system. There are two independent chambers at either
end of the piston-cylinder. The lower chamber is held at atmosphere or vacuum while the
pressure to be measured is applied to the upper chamber. The load cell is zeroed with a
pressure difference of zero across the piston (bypass open), taring out the weight of the
piston and coupling and other parasitic forces. Then, with the pressure bypass between the