4.4.2. General descriptions
The engine output is determined by the fuel delivery volume and engine efficiency.
To burn the supplied fuel completely to change into effective power for the engine, the volume
of air enough to burn the fuel completely should be supplied into the cylinders.
Therefore, the engine output is determined substantially by the cylinder capacity, and a
greater volume of compressed air is charged into cylinders of given capacity, the greater
engine output can be obtained as a greater volume of air charged into the cylinders burns so
much more fuel.
As explained, the compressing of air to supply into the cylinders is called “Supercharging” and
the making use of the energy of exhaust gas discharged from the combustion chamber to
charge the compressed air into the cylinders is called “Turbocharging”.
4.4.3. Functions
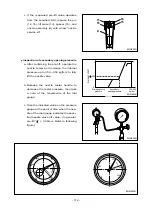
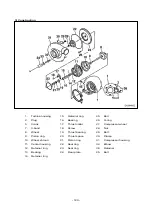
1) Turbine
Exhaust gas discharged from the combustion chamber distributes its own energy to the tur-
bine blades while passing the inside of the turbine housing, with the result that the turbine
shaft can get rotating force. This is the operating principle of ‘turbine’, which is mounted
with seal rings and heat protector to prevent exhaust gas from affecting the bearings
adversely.
2) Compressor
The compressor, which is connected to the turbine over the one and same shaft to form a
rotating body, takes in and compresses ambient air with rotating force transmitted from the
turbine shaft. Then, the compressed air is delivered to the intake stake. This is the operat-
ing principle of the compressor.
3) Bearings
(1) Thrust bearing
The turbine wheel creates thrust force. Therefore, exercise care so that the shaft is not
deviated from its the original position due to this thrust.
(2) Journal bearing
This journal bearing of floating type forms a dual oil film on both the inside and outside of
the bearing so that the bearing can rotate independently. As the dual oil film plays a role as
a damper, the sliding speed of the bearing surface becomes lower than the rotating speed
of the shaft, resulting in assurance of stability in its movement.
4) Sealing-Compressor shaft
The compressor is of a dual construction type composed of seal plate and seal ring to pre-
vent the leak of compressed air or lubricating oil.
- 121 -