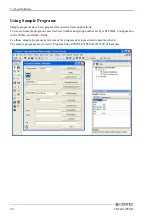
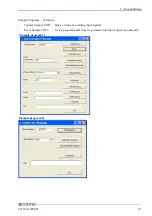
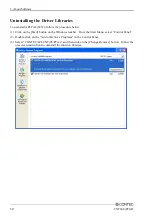
4. Function
CNT24-4(PCI)H
39
4.
Function
This section describes the features of the board.
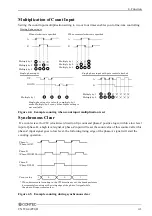
Types and Operations of Pulse Signals
Types of pulse signals
The following types of pulse signals (operation modes) can be set.
-
2-phase Input, Synchronous Clear, Multiply by 1
-
2-phase Input, Synchronous Clear, Multiply by 2
-
2-phase Input, Synchronous Clear, Multiply by 4
-
2-phase Input, Asynchronous Clear, Multiply by 1
-
2-phase Input, Asynchronous Clear, Multiply by 2
-
2-phase Input, Asynchronous Clear, Multiply by 4
-
Single-phase Input, Asynchronous Clear, Multiply by 1
-
Single-phase Input with Gate Control, Asynchronous Clear, Multiply by 1
-
Single-phase Input with Gate Control, Asynchronous Clear, Multiply by 2
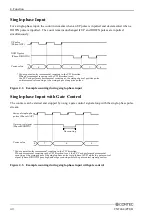
2-phase Input
Two-phase pulse input consists of a phase A pulse (advanced signal) and a phase B (delayed signal)
pulse that have 90 degrees of phase difference.
If the phase Z (reference position signal) is used, a Z pulse will reset count value of the two-phase pulse
input to zero.
0
1
2
* Count operation for incremental counting in the CW direction.
When decremental counting in the CW direction is set, the PC Card performs
decremental counting at the rising edge of the phase-A signal.
* The minimum phase difference between phases-A and B is 300 nsec.
Counting is not performed normally if the phase difference is less than 300 nsec.
Phase-A difference of 300 nsec is required.
Phase-A
(Phase-A/UP)
Phase-B
(Phase-B/DOWN)
Phase-Z
(Phase-Z/CLR)
Count value
Figure 4.1. Example counting during 2-phase input