Overview of the Cisco WMIC
Understanding the Cisco Mobile Wireless Network
4
Cisco 3200 Series Wireless MIC Software Configuration Guide
The Cisco 3200 Series routers at the primary intersections connect to the wireless backhaul by using an
integrated bridge.
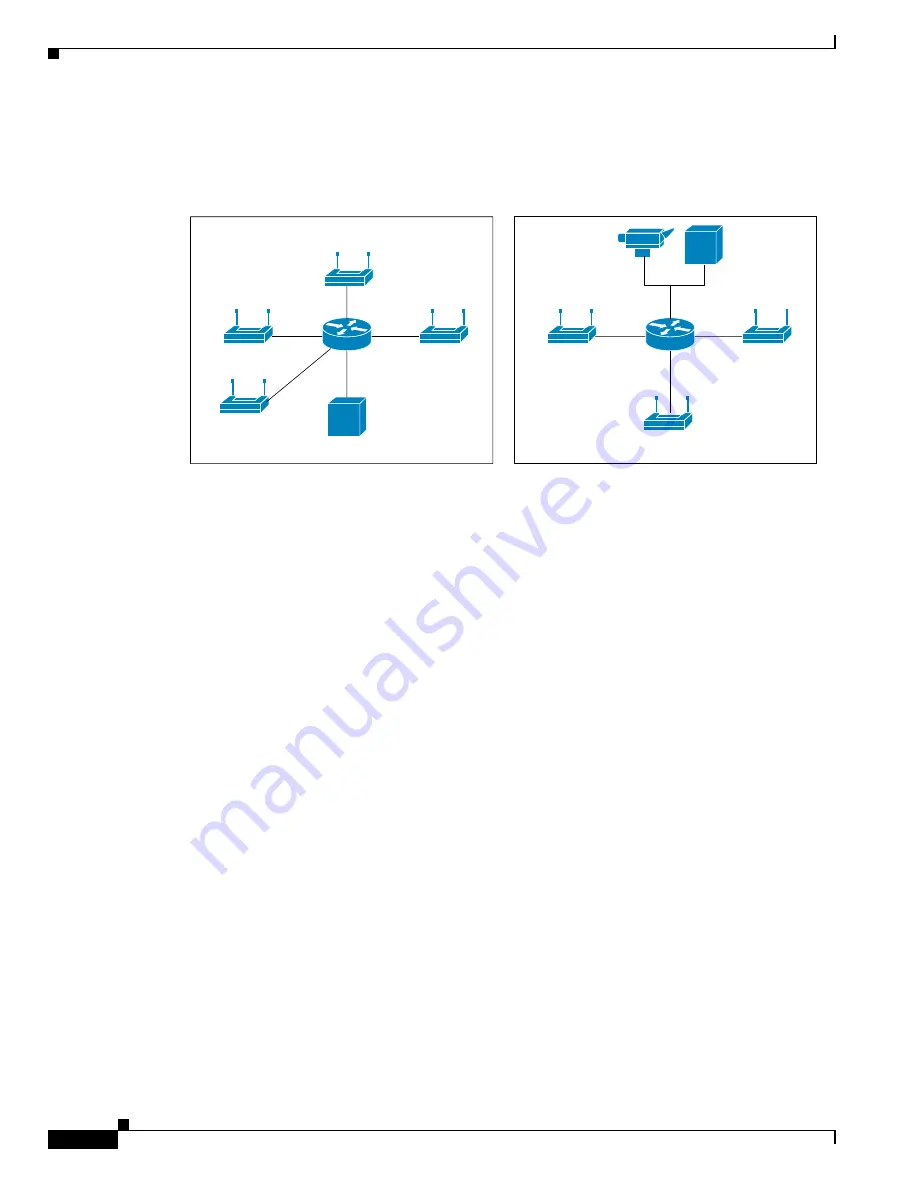
Figure 3
shows the intersection layout.
Figure 3
Primary Intersection and Secondary Intersection Layouts
This configuration supports a long chain of primary and secondary intersections. The number of
secondary intersections allowed between two primary intersections depends on factors such as
line-of-sight and bandwidth.
All secondary and primary intersections run an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP), so the path to every
primary and secondary intersection is advertised throughout the network. Applications, such as video
and data communications, can be accessed from anywhere in the network. When a packet from a mobile
unit arrives, the packet is forwarded to either end of the primary intersections in its cluster. The packet
takes the shortest path based on routing metrics.
To extend IP networks to various parts of the community and achieve sufficient bandwidth for the
required number of users and required applications, the Cisco Metro Mobile Network can use different
methods of backhaul, including a fiber network, leased lines, or broadband wireless bridging. Each
primary intersection has either a wireless or wired connection back to a nearby building.
Vehicle Network Example
A Cisco 3200 Series router installed in a mobile unit allows the client devices in and around the vehicle
to stay connected while roaming. WMICs in vehicle-mounted Cisco 3200 Series routers are configured
as access points to provide connectivity for 802.11b/g and 4.9-GHz wireless clients. Ethernet interfaces
are be used to connect any in-vehicle wired clients, such as a laptop or a camera, to the network.
Another WMIC is configured as workgroup bridge for connectivity to a root device at an intersection.
This allows it to transparently associate and authenticate through each root device in the architecture as
the vehicle moves about.
Serial interfaces provide connectivity to wireless WAN modems that connect to cellular networks that
use either CDMA or general packet radio service (GPRS). Wireless 802.11 connections are the preferred
service because they offer the most bandwidth; however, since a wireless connection is not always
available, cellular technology provides a backup link.
Figure 4
shows an example of the devices that can connect to the Cisco 3200 Series router in each mobile
unit.
Secondary
intersection
Non-root
SSID Infra24B
Non-root
SSID Infra24B
Root
SSID Infra24A
Root
SSID Infra224A
Controller
3200 FA
127850
Secondary
intersection
Non-root
SSID Infra24A
Root
SSID Infra24A
Root
SSID Infra24B
Controller
Camera
3200 FA
















































