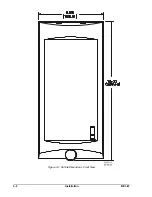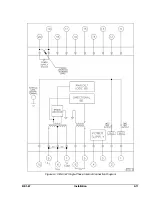
3-6
Functional Description
BE1-67
Push-to-Energize Output Contacts
If option 2-C has been selected, a small pushbutton switch is included for the time overcurrent functions and
if present for the instantaneous function. Each switch when depressed will energize the corresponding output
relay for testing purposes. To prevent accidental operation of these switches, they have been recessed behind
the front panel of the relay and are accessed by inserting a thin non-conducting rod through access holes in
the panel.
Appropriate power must be applied to terminals 3 and 4 (the relay power supply) for these pushbuttons to
operate the output relays. However, it is not necessary to apply currents and voltages to the sensing inputs
of the relay for these switches to function.
Power Supply Status Output
The power supply status output relay (option 3-3 and 3-4) has normally closed output contacts. This relay is
energized by the presence of nominal voltage at the output of the power supply. Normal operating voltage then
keeps the relay continuously energized and the contacts open. However, if the power supply voltage falls
below requirements, the power supply status output relay will de-energize and close the contacts.
A shorting bar is included in the relay case so that the status output terminals can provide a remote indication
that the subject relay has been withdrawn from the case or taken out of service by removing the connection
plug.
This output is not associated with any magnetically latched target. The POWER LED on the relay front panel
provides a visual indication of normal operating status of the power supply.
TARGET INDICATOR CIRCUITS
When the TARGET option is specified as either an A or a B, magnetically latched target indicators are
included within the relay. Targets are provided for the TIME overcurrent and the optional INST (instantaneous)
overcurrent functions. These targets may be actuated by either of two methods as defined by the style number
and explained in the following paragraphs.
Type A targets (referred to as INTERNALLY OPERATED) are operated by an internal driver circuit that is
actuated by a signal from the relay internal logic circuits. This type of target is tripped regardless of the current
level flowing through the output relay contacts. It is the only type of target that can be supplied if the output
contacts are specified as normally closed (output F).
Type B targets (referred to as CURRENT OPERATED) are operated when a minimum of 0.2 ampere flows
through the relay output contacts. To accomplish this, a special reed relay is placed in series with the output
contacts to provide the necessary signal to the target indicator. (The series impedance of the reed relay is less
than 0.1 ohm.)
Each target indicator is visible on the front panel of the relay with the cover in place. When operated, the disc
in the target changes from black to red and is magnetically latched in this position. To reset the target after
an abnormal system condition has been cleared, manually raise the target reset level on the front of the relay
or in the lower portion of the cover.
When targets are specified on single-phase relays (sensing input type A) only TIME and INST (instantaneous)
FUNCTION targets are provided. These targets may be either type A or type B.
Three-phase (Sensing Input type B) relays are supplied, when specified, with FUNCTION (TIME and INST)
targets and ELEMENT targets (A, B, C). The FUNCTION targets are either type A or type B as specified by
the style number. The ELEMENT targets are always type A (internally operated) targets.
Summary of Contents for BE1-67
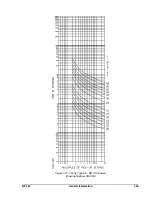
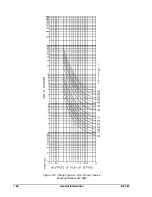
Page 23: ...BE1 67 General Information 1 17 Figure 1 13 Timing Type B2 Long Inverse Drawing Number 99 0931...
Page 26: ...1 20 General Information BE1 67 Figure 1 16 Timing Type B5 Inverse Drawing Number 99 0929...
Page 27: ...BE1 67 General Information 1 21 Figure 1 17 Timing Type B6 Very Inverse Drawing Number 99 0928...
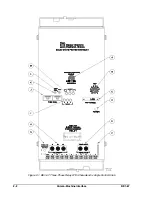
Page 39: ...2 6 Human Machine Interface BE1 67 Figure 2 3 Location of Assemblies Controls and Indicators...
Page 47: ...4 2 Installation BE1 67 Figure 4 1 Outline Dimensions Front View...
Page 48: ...BE1 67 Installation 4 3 Figure 4 2 Outline Dimensions Rear View...
Page 49: ...4 4 Installation BE1 67 Figure 4 3 Outline Dimensions Side View Semi Flush Mounting...
Page 50: ...BE1 67 Installation 4 5 Figure 4 4 Outline Dimensions Side View Projection Mounting...
Page 51: ...4 6 Installation BE1 67 Figure 4 5 Panel Drilling Diagram Semi Flush Mounting...
Page 52: ...BE1 67 Installation 4 7 Figure 4 6 Panel Drilling Diagram Projection Mounting...
Page 54: ...BE1 67 Installation 4 9 Figure 4 8 Single Phase AC Connections...
Page 55: ...4 10 Installation BE1 67 Figure 4 9 Three Phase AC Connections...
Page 56: ...BE1 67 Installation 4 11 Figure 4 10 BE1 67 Single Phase Internal Connection Diagram...
Page 57: ...4 12 Installation BE1 67 Figure 4 11 BE1 67 Three Phase Internal Connection Diagram...
Page 62: ...BE1 67 Testing 5 5 Figure 5 3 Blank Polar Graph Form Figure 5 4 Blank Polar Graph Form...