7
deutsch
7
E
Introduction
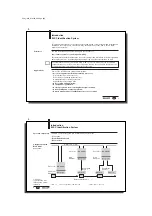
BIS C Identification System
Processor
I
NTER
B
US (remote bus or installation remote bus)
Data carriers BIS C-1_ _-...
Read/Write Heads
1)
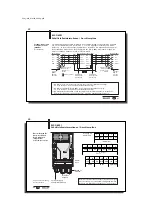
Schematic
representation of an
Identification System
(example)
1
) BIS C-3_ _ series, except BIS C-350 and -352
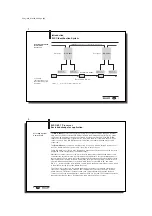
BIS C-6021
Processor
BIS C-6021
Configuration with
BIS C-6021
processor
C60_1-023_819395_0508_en.p65
8
8
E
BIS C-60_1 Processor
Basic knowledge for application
Selecting System
Components
The
BIS C-6001
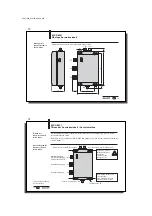
processor has a plastic housing. Connections are made through a terminal
strip, with the cables secured by PG fittings. A single read/write head from BIS C-65_ series
can be directly mounted to the processor, which creates a compact unit. If the BIS C-650
adapter is attached instead of the BIS C-65_ read/write head, two read/write heads may be
cable connected. If the BIS C-670 adapter is attached, one read/write head may be cable
connected.
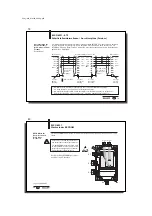
The
BIS C-6021
processor has a metal housing. Connection is made through round connec-
tors. Two read/write heads can be cable connected to the processor.
Series BIS C-60_1 processors have in addition a digital input. The input has various functions
depending on the configuration (see Parametering).
Whether the compact version of the processor with integrated read/write head makes sense
or whether the external solution is preferred depends primarily on the spatial arrangement of
the components. There are no functional limitations. All read/write heads are suitable for both
static and dynamic reading. Distance and relative velocity are based on which data carrier is
selected. Additional information on the read/write heads in series BIS C-65_ and series
BIS C-3_ _ including all the possible data carriers/read write head combinations can be found
in the manuals for the respective read/write heads.
The system components are electrically supplied by the processor. The data carrier repre-
sents a free-standing unit and needs no line-carried power. It receives its energy from the
read/write head. The latter constantly sends out a carrier signal which supplies the data
carrier as soon as the required distance between the two is reached. The read/write operation
takes place during this phase. Reading and writing may be dynamic or static.