The user can select whether there is a set time delay (called 'arcing time') between shots to burn the
fault-causing object from the line, or whether normal protection operating times are applied. When a
fault is not present when the breaker is closed but reappears soons after (called 'discrimination time'
and 'reclaim time'), the auto-recloser function can either arm another shot or give the final trip
command and the feeder becomes locked. The user can select the preferred method in the function's
settings.
It is difficult to define a typical auto-recloser scheme because the above-mentioned parameters (and
thus the main parameters of a scheme) vary greatly in distribution and transmission networks. This is
why there are no universally applicable answers from the number of shots and the duration of the dead
times to which protection functions should trigger the auto-recloser.
The minimum times for the "Dead time" setting is mostly dependent on the voltage level of the
protected network: the air needs enough time to de-ionize before the circuit breaker is opened. For
medium-voltage networks (20...75 kV) a 200 ms dead time should be sufficient. High-voltage networks
require a longer dead time: a 110 kV network needs 300 ms and a 400 kV network needs 400...500
ms. This minimum time is not, however, less straightforward than this as it is affected by other
parameters as well (such as conductor spacing, wind speed, fault type, fault duration, etc.). The main
purpose of the "Dead time" setting is to give enough time for the air surrounding the fault location to
return to its isolating state before the line is re-energized and therefore prevent the arc from reignite
due to the heated and ionized air. The circuit breaker's open-close-open cycle capacity is another
restricting factor for the minimum "Dead time" setting in low-voltage networks. In high-voltage
networks, the time de-ionizing requires puts additional limitations on the minimum "Dead time" setting.
The user can build different schemes for evolving faults (such as transient earth faults that become
multi-phase short-circuits or overcurrent faults) by changing the priorities and behaviors requests have.
The auto-recloser function has five (5) independent priority requests for reclosing: REQ1 has the
highest priority and REQ5 the lowest. The function also has one (1) critical request which halts the
reclosing in any position when the request is received.
Auto-recloser scheme in radial networks
A typical medium-voltage overhead network is usually radial in structure. This does not cause any
additional requirements for the auto-recloser scheme apart from the above-mentioned limitations from
the required air de-ionization time and the capacity of the circuit breaker. Also, a typical medium-
voltage overhead line consists only of consumers and has no power generation; thus, the main
objective of the structure is to provide a stable and continuous supply of electricity.
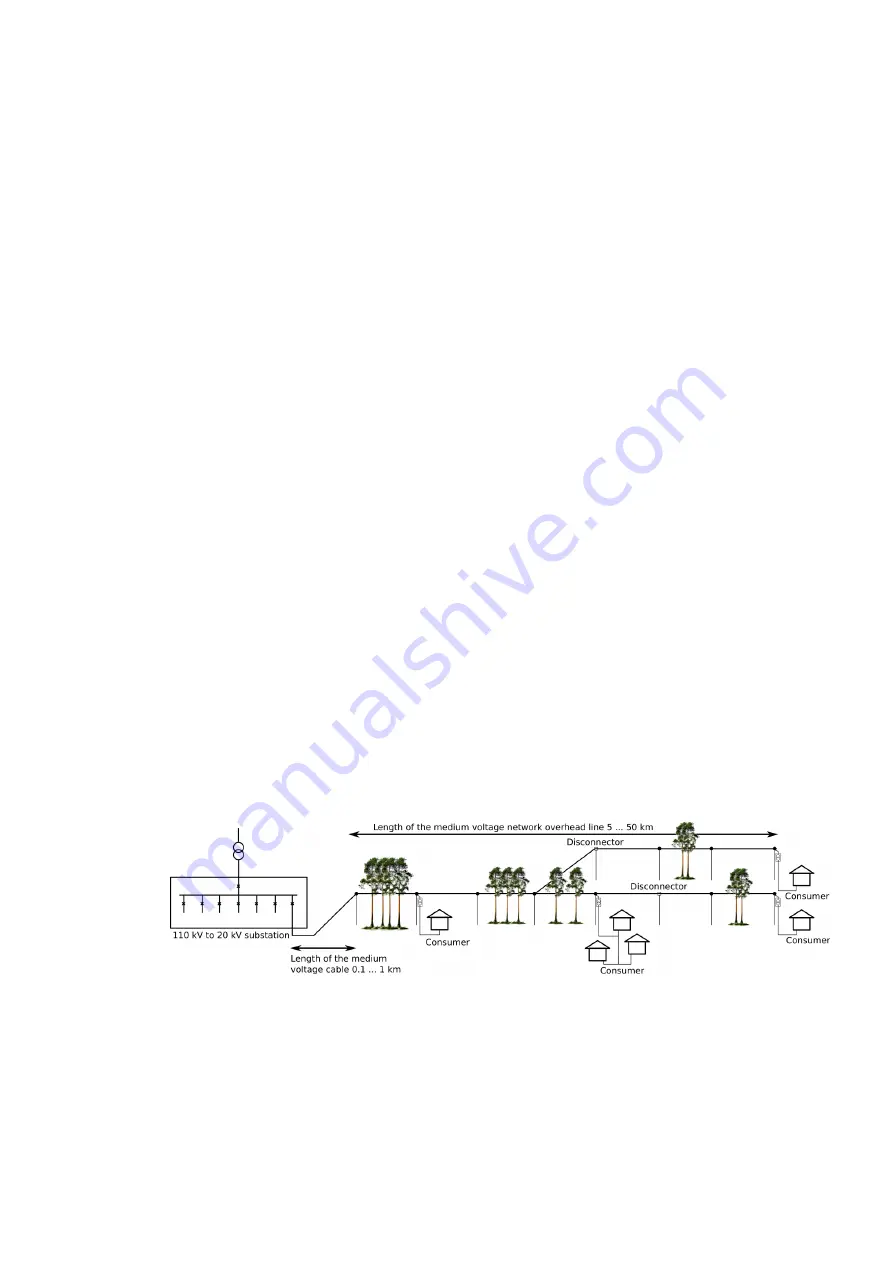
Figure. 5.4.4 - 187. Diagram of a typical radial medium-voltage network in rural areas.
Usually, a radially built medium-voltage network in rural areas consists of a short cable connection from
the substation to the overhead line, followed by a relatively long overhead line that normally ends with
the consumer. The consumer (residence, farm, etc.) can connect to basically any point in the overhead
line with a 20 kV/0.4 kV distribution transformer. The overhead line can have many branches, and it is
not uncommon (especially in rural areas) that there are multiple forest areas the line runs through
between the consumer connections. In longer lines in sparsely populated areas it is possible to isolate
areas of the overhead line by dividing it up with disconnectors (at least in branches).
A
AQ
Q-F215
-F215
Instruction manual
Version: 2.04
304






























