13
PUMP SHUTDOWN
1. Prior to disconnection of the motor power, ensure to close the process inlet isolation valve.
2. Where the process gas or vapor is in corrosive or hazardous nature, introduce inert gas, such as Nitrogen or Argon, into the
pump inlet for 20 to 30 minutes to purge out the residual process gas or vapor from the pump internals prior to disconnecting
the motor power. Please see Start/Stop (Clean) Purge section for more information.
3. Shutdown the pump.
4. Shut off the cooling liquid supply.
If the pump needs to be shut down for a long period of time when freezing weather is expected, and water is used as a cooling liquid,
the pump cooling jacket should be drained through the cooling jacket nozzles.
LUBRICATION
Lubricants for SDV pumps must be a
high-grade petroleum products containing
oxidation (and/or rust) inhibitor, extreme-
pressure additives etc. Lubricants
containing water, sulfate resin, or tar
should not be used with SDV pumps.
Turbine oil (ISO VG46) is readily
obtainable in the market and would
generally satisfy these requirements.
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
GENERAL
1. During normal operation, the temperature in the pump will increase in homogeneous matter as a result of compression
work done on the process gas or vapor. It is abnormal if the temperature rise is localized in the pump and/or the external
painting becomes scorched, however. The localized hot spots are typically due to the inadequate cooling liquid supply or
cooling liquid cut-off, interference of the screws with casing, or pump has ingested foreign material, such as sold particulates,
metal chips, process material build up etc. If a localized hot spot is observed, the pump must be shut down immediately for
inspection. In some cases, the screws and the casing may have become corroded. This corrosion will cause the clearance
between the screws and casings to increase and increase the “slip” (internal reverse flow: flow of gas from the pump
discharge to the suction). The pumping capacity of the pump is then decreased. In this case, the pump must be shutdown
and clearances must be measured and verified in order to determine required corrective actions.
2. Most of pump abnormalities can be noted by routine checks of bearing temperatures, vibration and noise etc. Daily
inspection of the pump is highly recommended as a preventative maintenance.
3. Interference between the pump screws or between the screws and the casing can be detected by listening through
stethoscope on the pump casing.
4. Whenever the pump is stopped, completely drain the cooling liquid if the pump is located in a cold region or in the winter to
prevent freezing of the cooling liquid.
PERIODIC INSPECTION SCHEDULE
DAILY
1. Check the electrical current load on the motor (Amps): An increase in the motor current load indicates abnormality of the
pump operation.
2. Check whether pump rotates smoothly and in correct direction (CW)
3. Check process inlet and discharge pressures
4. Check for the pump for any excessive noise and vibrations
5. Check NDE (Non Drive End) grease cover temperature
6. Check DE (Drive End), oil reservoir cover temperature
7. Check for any sign of cooling liquid leakage
8. Check oil level. High or low oil level can damage gears and bearings.
9. Check for any sign of external oil leakage.
10. Check cooling liquid supply flow rate and pressure.
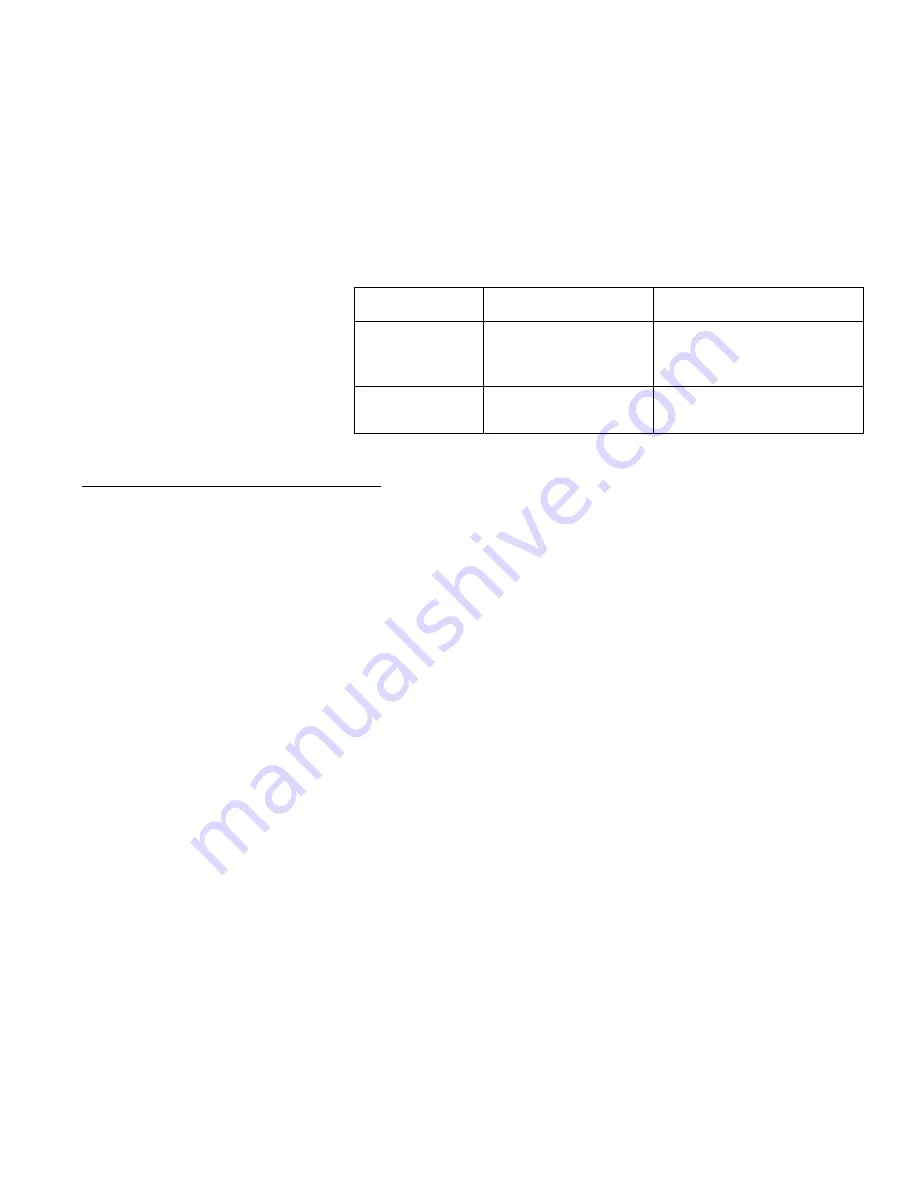
GEAR & BEARING
LUBRICANTS
OIL
GREASE
For General
Applications
BP, Energol THHT 46 / THB 46
Regal, R&O 46
Shell, Turbo 46
Mobil, DTE Oil Medium
Mobile 1 Synthetic Grease (Standard)
SHINETSU, G 40M
Nok-KLUBER, HFE 552
FAG, Arcanol L74V
For Special
Applications
Fomblin, 25/6, Krytox 1525
Fomblin, RT-15
Nok-KLUBER, Barrerta L55/2
Содержание KINNEY SDV SDV-120
Страница 28: ...28 NEW SDV 320 EXPLODED VIEW DRAWING NOTES ...




























