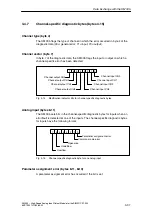
Special SM 335 Operating Modes
5-3
SM 335 – High-Speed Analog Input/Output Module for the SIMATIC S7-300
6ES7 335-7HG00-8BA1
5.2
“Comparator” mode
Introduction
Sometimes an analog value must be read frequently in order to make it possible to
react quickly when it reaches a specific value. In very high-speed processes, the
usual method employed by programmable controllers – read signal, process signal
in the CPU, output the response – is not fast enough. To help solve this problem,
the SM 335 has a special mode called “Comparator” mode.
Definition of comparator
A comparator, as its name implies, compares the measured analog value with a
specified analog value (called the comparison value). If the measured analog value
reaches the comparison value, the comparator initiates a specific response.
A comparison value can be specified for every two comparators.
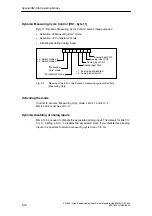
Two comparators
“Comparator” mode uses two comparators with different characteristic features.
Table 5-1
Characteristics of the two comparators
Comparator
Measures
End-of-cycle
interrupts
When the comparison value is reached
1
Analog input of
Comparator 1
Will continue to
be generated
•
The SM 335 outputs the specified analog values
to as many as three analog outputs
•
Generates a hardware interrupt
•
The SM 335 returns to “Free Cycle” or “Condi-
tional Cycle” mode
or
•
Switches over to Comparator 2
2
Analog input of
Comparator 2
Are sup-
pressed
•
The SM 335 outputs the specified analog values
to as many as three analog outputs
•
Generates a hardware interrupt
•
Writes the number of suppressed end-of-cycle
interrupts
•
Returns to “Free Cycle” or “Conditional Cycle”
mode
Detailed information about parameterizing in “Comparator” mode can be found in
Subsection 3.3.3.