Description of function
19
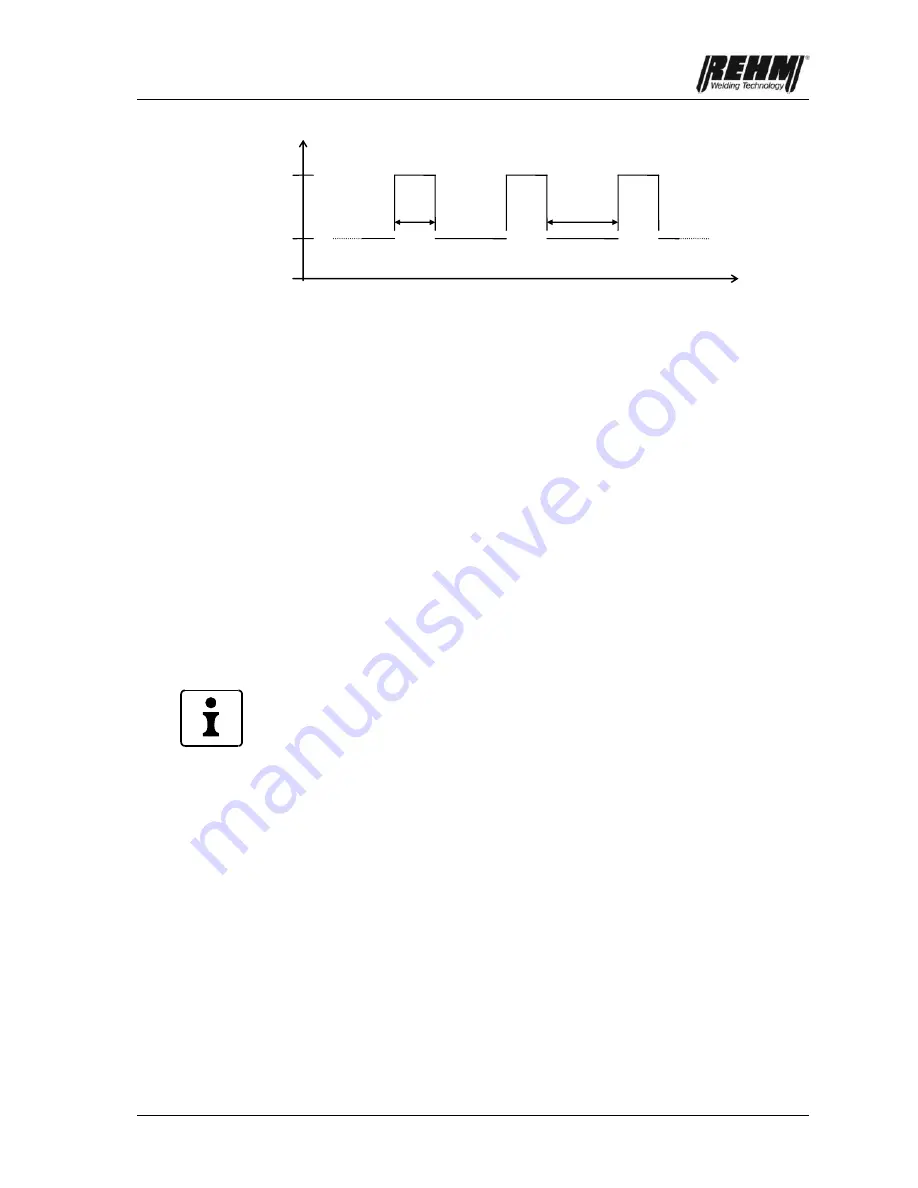
Fig 3.3: Welding current during pulsed welding
If a twin-button torch is used, pulsing can be switched off and also back on during
welding by pressing torch button 2. If torch button 2 is pressed while the welding
current is pulsing, pulsing is switched off and welding is continued using welding
current I2. This can for example be used to ensure that the lower welding current
I2 is used until a new filler metal is provided and welding is continued with
pulsing welding current by again pressing the torch button 2.
Conventional pulsing: Pulsing with pulse times greater than 0,1 second
The settings of the peak current time (t1) and the background current (t2) times
determine the time in which the peak current (I1) and the background current (I2)
is switched on and off. The digital display instrument always shows the currently
emitted welding current.
The welding current and the time for each pulse should be such that the
workpiece melts during the peak current phase and then is allowed to cool down
during the background current phase. Pulsed TIG welding allows the operator to
have better control of the welding pool under difficult conditions. Particularly
when for example, when welding out of position, bridging gaps, and welding thin
materials.
Note: If a twin button torch is being used, and button 2 is depressed during
pulsing, the pulsing will be switched off and the welding will continue with the
welding current setting I2. Depressing torch button 1 restores the pulsing process
once again.
High frequency pulsing: with a pulse frequency of 50 Hz up to 500 Hz
The welding current values set for the current I1 and I2 determine the pulse
amplitude. The active time for duration of these current settings is equal. With HF
pulsing switching from one current level to another occurs very quickly, hence the
name high frequency pulsing.
In order to calculate the pulse frequency, the following relationship exists
between the pulse timing t1 and t2:
Total pulse time = I1-Pulse time + I2-Pulse time = 1 / Pulse frequency
I1-Pulse time
= I2-Pulse time
= 0,5 * Total / Pulse time
Example:
Pulse frequency = 50 Hz
Total Pulse time = I1-Pulse time + I2-Pulse time = 1 / 50 Hz = 20 ms = 0,02 s
I1-Pulse time = 0,5 * Total Pulse time = 0,01s
I2-Pulse time = 0,5 * Total Pulse time = 0,01s
This means that the welding current has the value set for I1 for 0,01 s (=10 ms)
and that the welding current has the value set for I2 for 0,01 s (=10 ms), the
switching from once current to the other continues ad. Infinitum.
Current I1
Current I2
Pulse time I1
Pulse time I2
Time
0
Содержание 150 3310
Страница 1: ...GB OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS TIG welding units TIGER 170 210 DC AC DC SET...
Страница 7: ...Introduction 7 1 2 General description Fig 1 1 TIGER 170 DC and Tiger 210 AC DC...
Страница 57: ...Spare parts 57 10 2 Machine components photographs 2...
Страница 58: ...Spare parts 58...
Страница 63: ......
















































