Project configuration
Operating Manual PSEN op2B/1 Series
1003357-EN-02
27
5.3
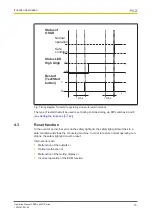
Distance from reflective surfaces
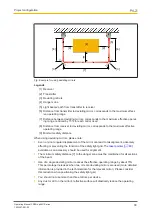
If there are reflective surfaces close to the beams emitted from the safety light grid (whether
from above, below or from the side) passive reflections can mean that an object within the
protected field is not detected (see diagram).
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
Fig.: Interference to the function of the safety light grid due to reflective surfaces
Legende
[1] Transmitter
[2] Receiver
[3] Reflective surface
[4] Danger zone
[5] Distance from safety light grid
to reflective surface
α Opening angle of the light beams emitted by the
safety light grid
The receiver would detect the reflection from the reflective surface as a
secondary beam,
even if the main beam is interrupted by an existing object requiring detection.
As a result, the safety light grid
must be installed at a minimum distance from reflective sur-
faces.
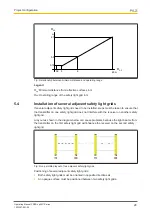
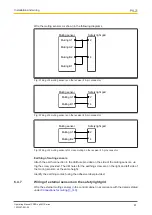
The minimum distance depends on two factors:
}
Operating range between transmitter and receiver
}
Maximum opening angle of the light beams emitted by the safety light grid
– 10° = ± 5° in relation to the optical axis
The formula for calculating the minimum distance D
SR
is:
}
Operating range < 3 m: 0.27 m
}
Operating range ≥ 3 m: 0.5 x D
OP
in m x tan 2α