16
4.4. Gas Type Dependent Operations
Water cooling is required if the pumps are to be
operated with gas load.
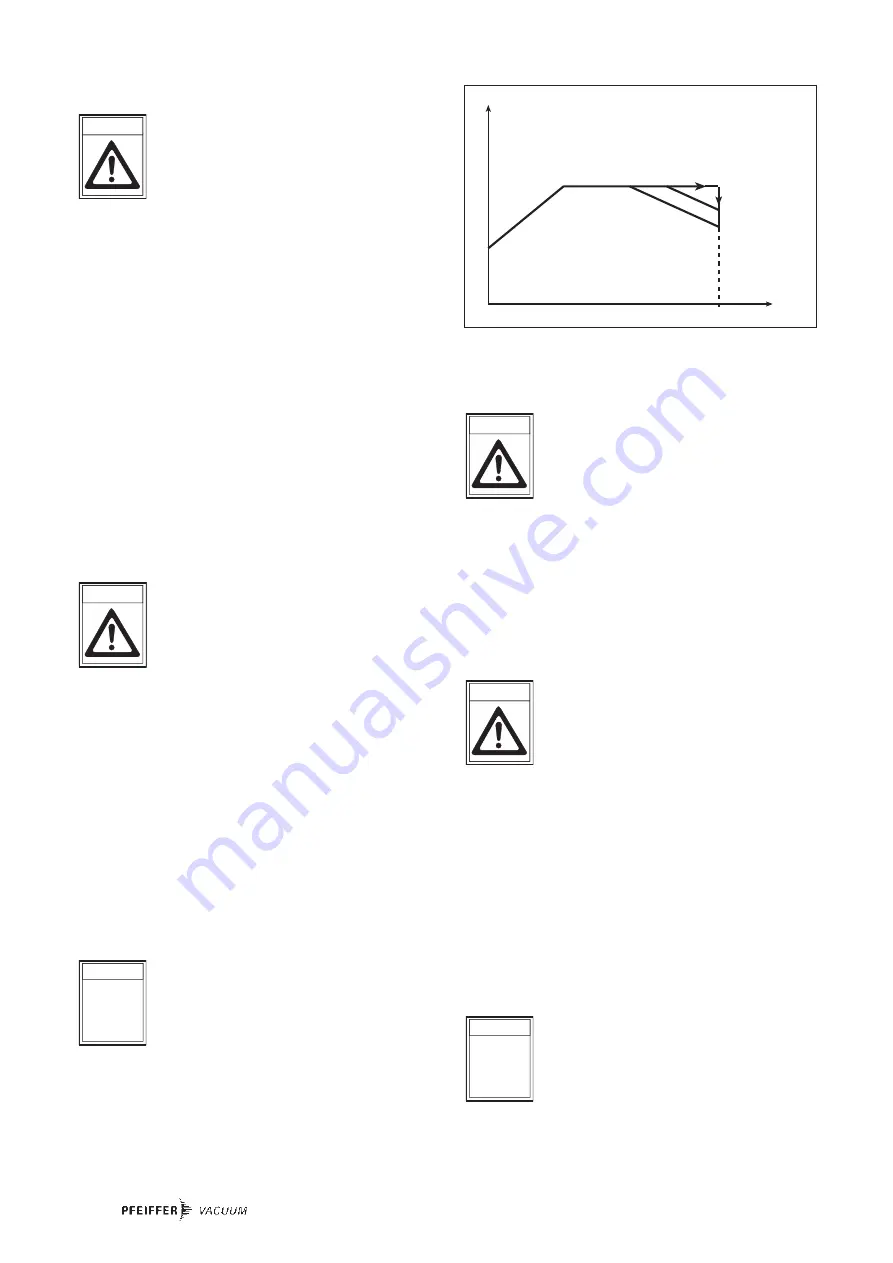
Where high level gas loads and rotation speeds are involved,
the resulting friction subjects the rotor to the effect of great
heat. To avoid over-heating, a power rotation speed
characteristic line is implemented in the TC 600; this ensures
that where maximum gas loads are involved, the pump will
operate at any rotation speed without the danger of damage
arising.
The maximum power is dependent on the type of gas. Two
characteristic lines are available for any type of gas in order
to fully exploit the power potential of the pump:
– "Gas-Mode 0" for gases with molecular mass
≥
40 as, for
example, Argon;
– "Gas-Mode 1" for all lighter gases.
Works setting: “Gas mode 0”
➡
Set the applicable gas mode on the TC 600 via the
DCU/HPU (please refer to the respective operating instruc-
tions.
Pumping gases with molecular mass
≥
40 with
the incorrect gas mode can cause damage to
the pump.When pumping noble gases heavier
then Argon it can come to the destruction of the
pump. Please contact the manufacturer before
using such gases.
For the vertex of the power characteristic line please refer to
Section 9. Technical Data.
Maximum power is applied when the pump starts in order to
limit the time required. Once the set rotation speed is
attained, switching to the selected power characteristic line
is automatic. If the gas dependent maximum power is excee-
ded, the rotation speed is reduced until equilibrium between
the permissible power and gas friction is attained.
The power limitation serves to protect the pump against ther-
mal over-loading. In order to avoid rotation speed fluctuations
it is recommended to set, in rotation speed setting mode, the
equilibrium frequency or a somewhat lower frequency.
There can be types of pump whereby there is no
differentiation between the two ”gas modes”
settings.
☞
PLEASE NOTE
WARNING
CAUTION
4.5. Shutting Down For Longer Periods
If aggressive or hazardous gases are pumped
there is a danger of personal injury resulting
from coming into contact with process gases.
Before removing a turbopump from the system,
first:
–
Vent the turbopump with a neutral gas or
dry air.
– Ensure that there is no residual process gas in the system
nor in the feeder lines.
If the turbopump is to be shut down for more than a year:
➡
Remove turbopump from the system.
➡
Change the lubricant reservoir (see Section 7.1.).
Lubricant TL 011 should not be used when there
have been no operations for 33 yye
ea
arrss..
➡
Close the high vacuum flange and evacuate the turbopump
via the fore-vacuum flange.
➡
Vent turbopump via the venting connection with nitrogen
or dry air.
➡
Close fore-vacuum and venting connection by blank
flanging.
➡
Place the pump vertically on its rubber feet.
➡
The pump must be stored in buildings within a temperature
range of -25 °C to +55 °C.
➡
In rooms with moist or aggressive atmospheres, the turbo-
pump must be air-sealed in a plastic bag together with a
bag of dessicant, e.g silicagel.
If the pump has been shut down for
3 years
, the bearing must be changed (please
contact Pfeiffer Vacuum Service).
☞
PLEASE NOTE
CAUTION
WARNING
Power
Frequency
D
B
C
A
D-C = Gas mode «0»
B-A = Gas mode «1»
Run up
fnom
Gas type characteristic line
















































