© 2020 Copyright Newmar Corporation. All rights reserved. For the most up-to-date version of this content, and for more product-specific information, please refer to Newgle.
69
ELECTRICAL
GROUND FAULT CIRCUIT INTERRUPT
(GFCI) OUTLETS
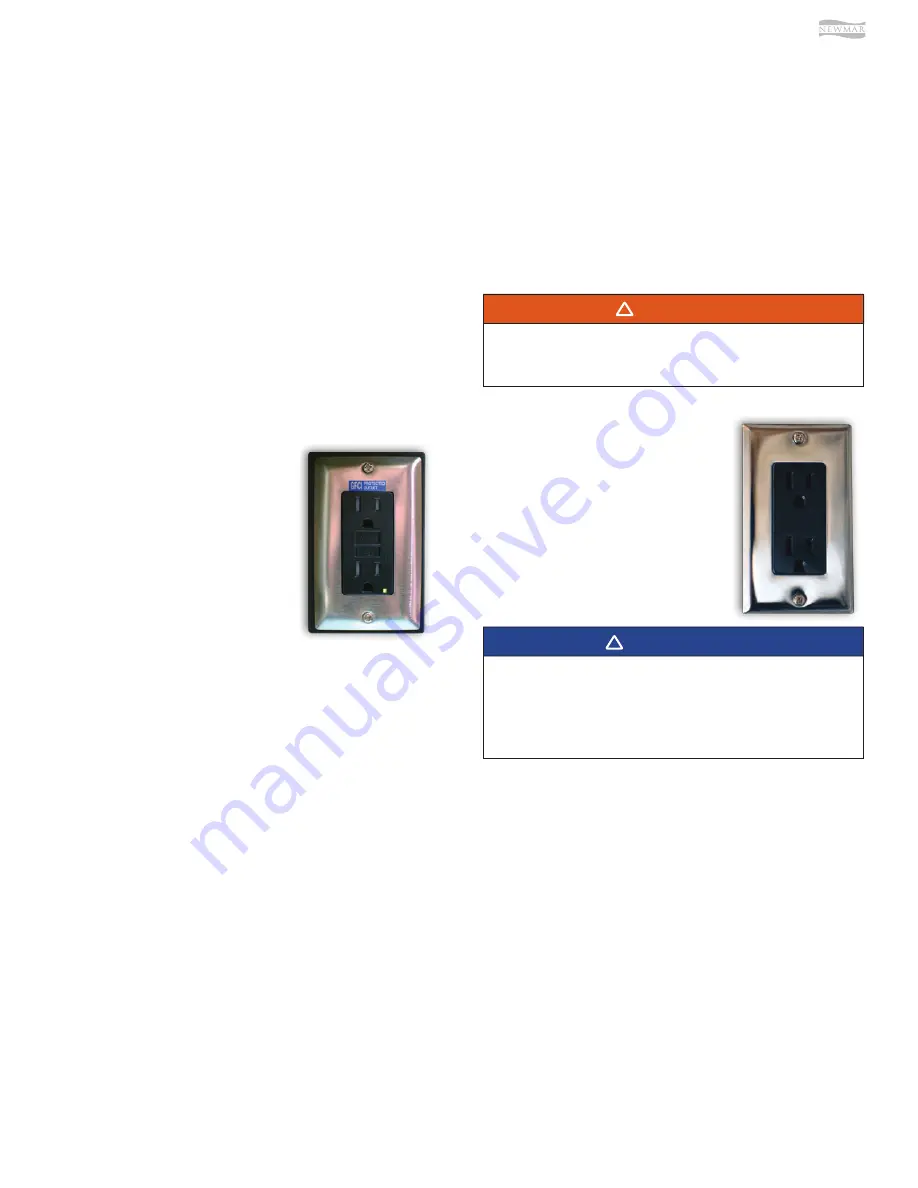
The Ground Fault Circuit Interrupt
(GFCI) outlets protect the user
from ground faults between a hot
wire and ground. The 120 Volt
electrical outlets in the kitchen
and bath area are GFCI protected
receptacles. The electrical outlets
located in the Slideouts are wired
through the kitchen GFCI. The
exterior electrical outlets are wired
through the bathroom GFCI. On
units equipped with the floor heat
option, a separate GFCI is installed in the bathroom or
near the main breaker box. Units with the holding tank
heat pad option will have an additional GFCI located in
the basement area; however, the exact location varies.
THREE-STAGE CHARGING PROCESS
The charging cycle uses three states: bulk, absorption,
and float. During the initial bulk stage, the inverter
charges at near its full current ability. This causing the
battery voltage to rise over time. After the battery voltage
reaches the bulk voltage setting, the charger starts the
absorption stage.
During this phase, the charge rate is gradually reduced
while the battery voltage is held near the bulk voltage
setting. This insures that the battery is fully charged. The
float stage is initiated when the battery has been held
at the bulk voltage setting for the absorption period.
At this point the battery voltage is allowed to fall to the
float voltage setting, where it is maintained until another
charge cycle is initiated. This reduces gassing of the
battery and keeps it fully charged. A new three stage
charging cycle is initiated after an AC source is reapplied
to the AC input terminals.
The GFCI will not reduce the shock hazard if the
short is between a neutral and hot wire or two hot
load wires.
WARNING
!
Do not use an adapter, cheater, or extension cord
that breaks the continuity of the ground circuit
to the ground pin. Never remove the ground
pin from a plug in order to connect it to a two-
pronged ungrounded outlet.
IMPORTANT
!
120 VOLT OUTLETS
Several 120 volt receptacles are
located throughout the interior of
the unit. These receptacles require
three-pin plugs that provide proper
grounding to protect you from
electrical shock. The breaker for
the outlets are usually located in
the breaker box. If the breakers are
on the inverted circuitry, they will
be located in the subpanel near the
main breaker box.
The GFCI outlets should be tested at least once a month.
The 120 Volt electrical system must be energized in order
to test the GFCI. The reset button needs to be pressed
before starting the test. Then push the test button, which
will cause the reset button to pop out, confirming the
protected circuits have been disconnected. Push the
reset button again until a click is heard to reactivate
the protected circuit. If the GFCI is working properly,
the reset button will remain in the “IN” position. If an
item plugged into a Slideout or outside receptacle is
not working, check for a tripped GFCI in the kitchen or
bathroom. Likewise, if the floor heat or holding tank heat
pads are not working, check the GFCI for that circuit.
Electrical Typical Amp Draw List
This article provides a basic overview of the typical amp draw of electrical components and appliances in a coach.
Knowing and understanding the electrical terminology, as well as the average amperage (current draw) of all the electrical
appliances in your coach, can help you manage electrical use and prevent the inconvenience of tripping a breaker.
Amp Draw
Do you know how many Amps you are using at any single
moment? It is surprising how quickly the current draw
(Amps) of your appliances can add up for your coach’s
30 or 50 Amp system. Knowing and understanding the
electrical terminology, as well as the average amperage
(current draw) of all the electrical appliances in your
coach, can help you manage electrical use and prevent
the inconvenience of tripping a breaker.
Below is a list of the typical appliances used and the
approximate amps required to operate them.
•
V = volt; volt is the measurement of electrical pressure
•
A = amp; amp is the measurement of electrical current
(volume) used by an electrical device.
•
W = watt; watt is the measurement of how much
electrical work is being done.
Содержание London Aire 2021
Страница 1: ...2021 sm...






































