Chapter 3
Hardware Overview
3-4
www.ni.com
RTSI Bus
The seven trigger lines on the RTSI bus provide a flexible interconnection
scheme between multiple 1408 devices as well as between any National
Instruments DAQ devices and the 1408 device.
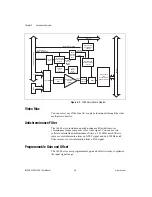
Trigger Control and Mapping Circuitry
The trigger control and mapping circuitry routes, monitors, and drives the
external and RTSI bus trigger lines. You can configure each of these lines
to start or stop acquisition on a rising or falling edge. In addition, you can
drive each line asserted or unasserted, similar to a digital I/O line. You
can also map onboard status values (HSYNC, VSYNC,
ACQUISITION_IN_PROGRESS, and ACQUISITION_DONE) to the
lines.
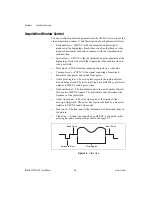
Acquisition and Region of Interest Control
The acquisition and region of interest control circuitry monitors the
incoming video signal and routes the active pixels to the FIFO buffers. The
1408 device can digitize an entire frame and perform pixel and line scaling
and region-of-interest acquisition. Pixel and line scaling lets certain
multiples (2, 4, or 8) of pixels and lines to be transferred to the PCI bus. In
region-of-interest acquisition, you select an area in the acquisition window
to transfer to the PCI bus.
FIFO Buffer
The 1408 device uses a 4 KB FIFO buffer for temporary storage of the
image being transferred to the PCI system memory or display memory.
The buffer stores six full video lines during image acquisition.
Scatter-Gather DMA Controllers
The PCI/PXI-1408 uses three independent onboard direct memory access
(DMA) controllers. The DMA controllers transfer data between the
onboard FIFO memory buffers and the PCI bus. Each of these controllers
supports scatter-gather DMA, which allows the DMA controller to
reconfigure on-the-fly. Thus, the 1408 device can perform continuous
image transfers to either contiguous or fragmented memory buffers.