84
Appendix C: Tuning Your System
The subscripted n represent the sample period. The terms are defined:
Sn = Sn-1 + En if -Smax < Sn < Smax
Smax if Sn > Smax
-Smax if Sn < -Smax
On = DAC output
KR = overall scale factor
Kp = proportional gain
Kd = derivative gain
Ki = integral gain
Kv = velocity feed-forward
Ka = acceleration feed-forward
Ko = static DAC offset
Kf = friction feed-forward
En = position error
Mn = 0 or 1 based on the command velocity
Vn = command velocity
An = command acceleration * 2-6
Sn = integrated error
Smax = maximum integrated error
Each coefficient can be adjusted using the SETUP program and is explained in the following
sections.
C.2 Tuning Parameters
C.2.1 Proportional Gain (K
p
)
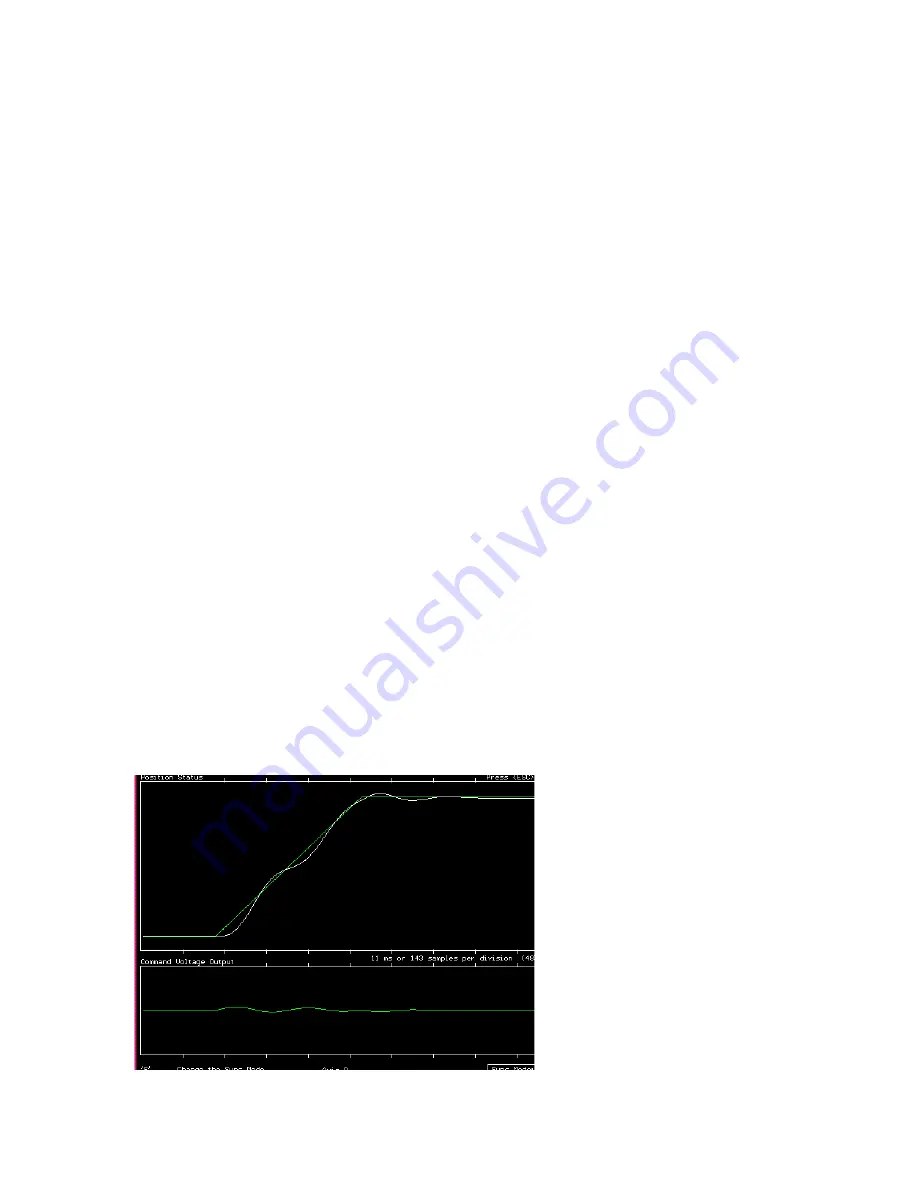
This term determines the overall response of a system to position errors. A low Proportional
Gain provides a system which is very stable (doesn't oscillate), has low stiffness and large
position errors under load. A high Proportional Gain provides high stiffness and small position
errors under load but may oscillate.
Typical gain values are 100-500 for velocity (voltage) controlled servos and 500-2000 for torque
(current) controlled servos. Closed loop step systems are similar to velocity controlled servos.
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com










































