47
7.3.3.1.3 Data format types
BIN
(binary format) Decimal numbers are encoded by bit weight
15
0
215 214 213 212 211 210 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20
BCD
(binary coded decimal format) Decimal numbers are encoded by bit weight per 4-bit nibble
15
12 11
8 7
4 3
0
10
3
10
2
10
1
10
0
For example: The Read address raw data is
0000 0100 0010 0101
.
The
BIN
format treats the data as
1061
The
BCD
format treats the data as
425
7.3.3.1.4 Attributes
Some Parts have Attribute parameters on the General Tab. Select the desired attribute from the dropdown and fill in
any information required. The attributes vary from part to part. Reference Section 3, Object Reference Guide, for
complete details about a Part’s attributes.
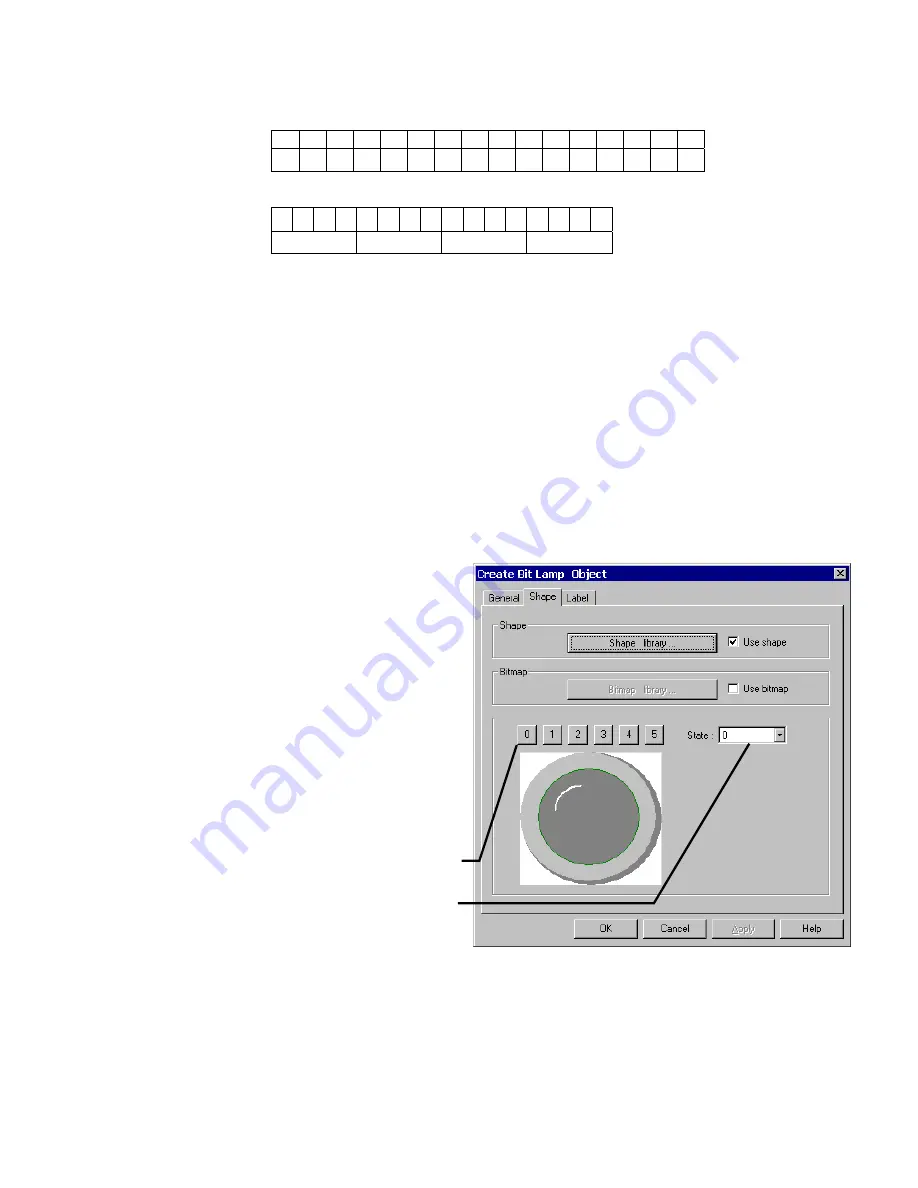
7.3.3.2 The Shape Tab
The Shape tab is used to assign a graphic background to an object. If no graphic is assigned then the object has a
transparent background. A frame is shown on the project window to indicate that a part is present. The frame is not visible in
simulations or the MMI.
Selecting a Shape or Bitmap
1. Click on the
Shape
tab
2. Select
Use shape
or
Use bitmap
3. Click
Shape library
or
Bitmap library
The shape/bitmap browser pops up. Select the desired
shape/bitmap. Shapes are stored in shape libraries (*.slb
files). Bitmap graphics are stored in Bitmap libraries (*.blb
files).
A maximum of 10 libraries can be attached to a project. By
calling up different shape or bitmap libraries, useful
graphics for almost any application can be found. Users
can also build up their own shape and bitmap libraries.
Note:
If both shape and bitmap are selected for a part, the graphic shown in the preview box is the one displayed on the
window at run time. (Usually the Shape takes precedence.)
Note:
Reference the Library Operations section for full details about the Library features.
Bit number
Weight
The
State
dropdown can be used to view
additional states of the selected shape.
The
State
select buttons can be used to view
the various states of the selected shape.
Содержание MMI-1500
Страница 2: ...ii...






























