Basically, frequency modulation is an analogue process to create complex waveforms/sounds.
It got more widespread once digital sound processing started to develop, as digital oscillators
are more stable than analogue ones. This stability is needed to create harmonic sounds instead
of just noise-alikes.
The FM that is offered in the SUNSYN is a complementary feature, which greatly expands
the sonic possibilities, especially for creating sounds with noise-contents.
You need two oscillators. The first one (the modulator) modulates the frequency of the
second one (the carrier). The resulting waveform contains harmonics that can not be found in
the basic signals. The spectrum is extended by an
amount of so-called disharmonic frequency structures.
Such a harmonic structure can’t be created through
the normal use of oscillators and filters
(subtractive synthesis).
By carefully altering the frequency of the modulator
and the intensity of the modulation, you can control the harmonic structure/contents of the
resulting sound.
You can experiment with the frequencies (Range, Semitones and cents) to change the sonic
characteristics. E.g. when the modulating frequency (source) is lower than the carrier
(destination), then inharmonic overtones and therefore noise-alike sounds are created. The FM
feature of the SUNSYN can create lots of different noise-alike sounds very easily. The spec-
trum ranges from metallic, bell-alike sounds to undefinable noise. Experiment with the diffe-
rent settings of the oscillators. Small changes of
(Semitone)
and
(Range)
can already cause
radical sonic variations. Using different waveforms or the pulsewidth feature is also very
interesting!
The filter cutoff frequency can be voltage controlled as we already know. The most simple
example is to let envelope 1 control the cutoff frequency or to set up a control element which
controls it (e.g. LFO, when we choose VCF CUT as destination).
Next to this you can use an audio signal to modulate the cutoff of the VCF. When the
resonance parameter is high enough so that the VCF is self-oscillating (pumping), you get
again – FM.
In this way, the self-oscillating VCF works as carrier, the audio signal that is routed to VCF
CUT is the modulator.
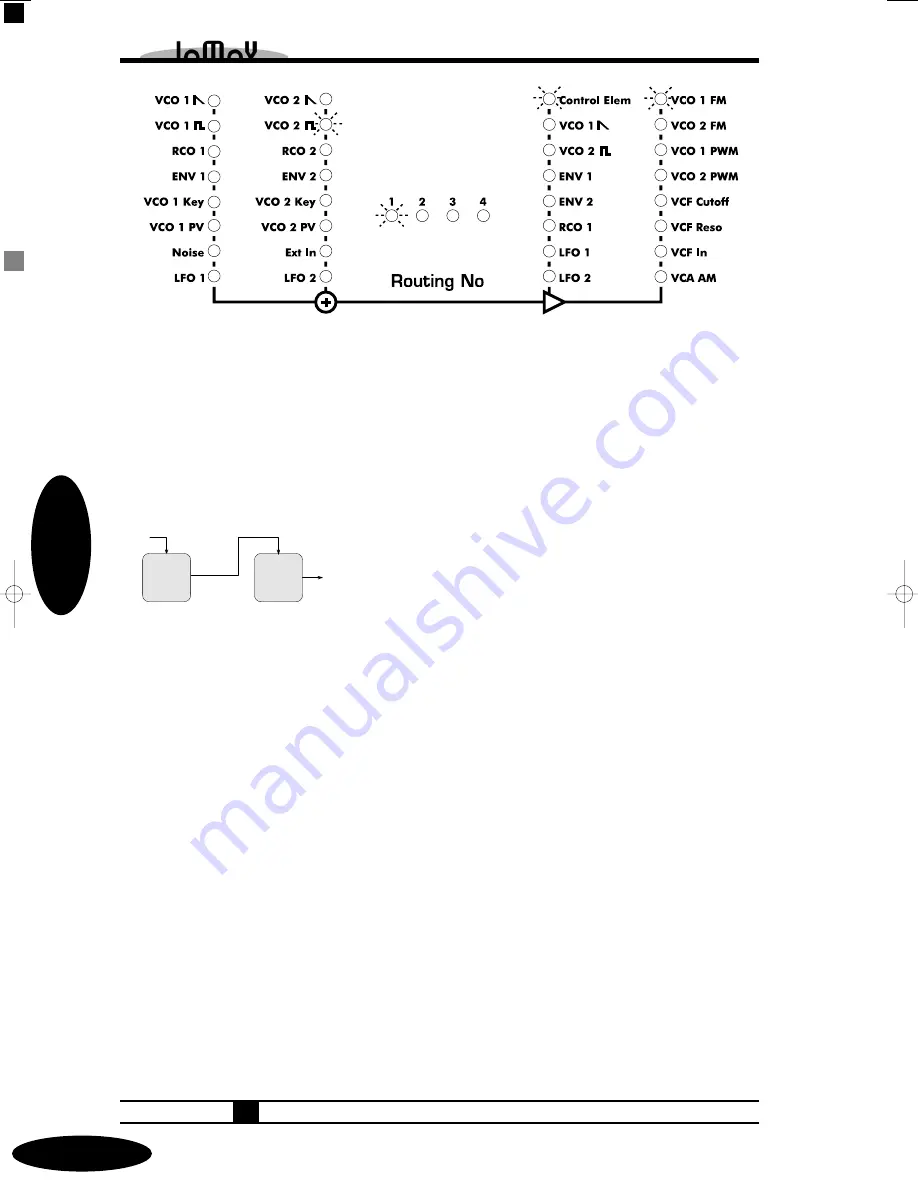
Routing Elements
3-10
056
Single Mode
OSC 2
Carrier
OSC 1
Modulator
thebook-all 07.11.2002 18:28 Uhr Seite 56 (Schwarz Bogen)










































