211
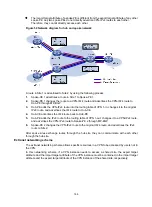
Figure 64 Network diagram for BGP/OSPF interaction
As shown in
, CE 11, CE 21, and CE 22 belong to the same VPN and the same OSPF
domain.
Before domain ID configuration, VPN 1 routes are advertised from CE 11 to CE 21 and CE 22 by
using the following process:
1.
PE 1 redistributes OSPF routes from CE 11 into BGP, and advertises the VPN routes to PE 2
through BGP.
2.
PE 2 redistributes the BGP routes to OSPF, and advertises them to CE 21 and CE 22 in AS
External LSAs (Type 5) or NSSA External LSAs (Type 7).
After domain ID configuration, VPN 1 routes are advertised from CE 11 to CE 21 and CE 22 by using
the following process:
3.
PE 1 redistributes OSPF routes into BGP, adds the domain ID to the redistributed BGP VPNv4
routes as a BGP extended community attribute, and advertises the routes to PE 2.
4.
PE 2 compares the domain ID in the received routes with the locally configured domain ID. If
they are the same and the received routes are intra-area or inter-area routes, OSPF advertises
these routes in Network Summary LSAs (Type 3). Otherwise, OSPF advertises these routes in
AS External LSAs (Type 5) or NSSA External LSAs (Type 7).
Routing loop avoidance
Figure 65 Network diagram for routing loop avoidance