189
The second method distributes traffic of a single VPN to multiple tunnels. The transmission delays on
different tunnels can vary by a large amount. Therefore, the destination device or the upper layer
application might take a great time to sequence the packets. As a best practice, do not use the
second method.
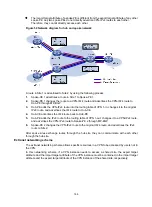
Figure 47 MPLS VPN tunnel selection diagram
Configuration procedure
To configure a tunnel policy:
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2.
Create a tunnel policy, and
enter tunnel policy view.
tunnel-policy
tunnel-policy-name
By default, no tunnel policies
exist.
3.
Configure tunnel selection
methods.
•
(Method 1) Configure a
tunnel as a preferred tunnel:
preferred-path
tunnel
number
•
(Method 2) Configure the
tunnel selection order and
the number of tunnels for
load balancing:
select-seq
{
cr-lsp
|
gre
|
lsp
} *
load-balance-number
number
Configure one or both methods.
By default, no preferred tunnels
are configured.
By default, only one tunnel is
selected in LSP—GRE—CRLSP
order.
NOTE:
For a VPN to exclusively use a tunnel, you can specify the tunnel as the preferred tunnel in a tunnel
policy, and apply the policy only to that VPN.
Displaying tunnel information
Execute
display
commands in any view.
Task Command
Display tunnel information.
display mpls tunnel
{
all
|
statistics
| [
vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name
]
destination
{
ipv4-address
|
ipv6-address
} }