441
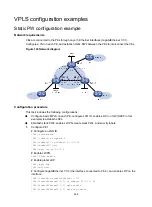
Figure 118 Source MAC address learning on a PE
The MAC address table uses an aging timer for each dynamic MAC address entry. If no packet is
received from a MAC address before the aging timer expires, VPLS deletes the MAC address.
When an AC or a PW goes down, the PE deletes MAC addresses on the AC or PW. Then it sends an
LDP address withdrawal message to notify all other PEs in the VPLS instance to delete those MAC
addresses.
Unicast traffic forwarding and flooding
After a PE receives a unicast packet from an AC, the PE searches the MAC address table of the VSI
bound to the AC for packet forwarding.
•
If a match is found, the PE forwards the packet according to the matching entry. If the outgoing
interface in the entry is a PW, the PE inserts the PW label to the packet, and adds the public
tunnel header to the packet. It then forwards the packet to the remote PE over the PW. If the
outgoing interface in the entry is a local interface, the PE directly forwards the packet to the
local interface.
•
If no match is found, the PE floods the packet to all other ACs and PWs in the VSI.
After a PE receives a unicast packet from a PW, the PE searches the MAC address table of the VSI
bound to the PW for packet forwarding.
•
If a match is found, the PE forwards the packet through the outgoing interface in the matching
entry.
•
If no match is found, the PE floods the packet to all ACs in the VSI.
Multicast and broadcast traffic forwarding and flooding
After a PE receives a multicast or broadcast packet from an AC, the PE floods the packet to all other
ACs and the PWs in the VSI bound to the AC.
After a PE receives a multicast or broadcast packet from a PW, the PE floods the packet to all ACs in
the VSI bound to the PW.