G-2
Glossary
IEEE 488-1978 interface
A parallel
interface standardized by Electronic Industries
Association Standard 488-1978.
initialize
To set plotter conditions to known
default values.
interface
Anything (a cable, for example)
used to join components of a computer system
so they function in a compatible and
coordinated fashion. Also, standards which
allow systems to connect with each other
(e.g., HP-IB, RS-232-C).
I/O error
A data transmission error
between a computer and a peripheral.
Examples of I/O errors are mismatched
interface conditions, such as baud rate and
parity.
menu
Messages and options displayed on
the plotter’s front-panel display.
nest
A group of compatible plots arranged
next to each other horizontally/vertically to
save media when plotted.
A collection of interconnected,
individually controlled computers, together
with the hardware and software used to
connect them. A network allows users to
share data and peripheral devices such as
printers and storage media, to exchange
electronic mail, and so on.
overflow
To exceed the capacity of a
buffer’s storage space. When a buffer
overflows, the excess data is lost.
palette
A set of sixteen pens (numbered 0
through 15) for which width and % shading
are defined from the plotter’s front panel.
parallel interface
An interface type in
which a separate wire is used for each data bit
in a byte or word and all bits are transferred
simultaneously. HP-IB and Centronics are
parallel interfaces.
parity
An error-checking method for
information transfer between a computer and
a peripheral device. Parity is used to check the
accuracy of binary data.
peripheral (device)
A device separate from,
but used with, a computer. For example, a disc
drive, printer, or plotter.
queue
Order in which plot data is received.
raster
1. A matrix of dots, or pixels, where
each pixel is defined by a bit. A bit that is
“on” will print a dot on the paper. A bit that is
“off” will leave the area blank. 2. A method
for defining a plot directly in terms of the
pixels rather than as vectors.
repeatability
A measure of how closely a
device can return a pen to the previously
plotted point.
resolution
A measure of image sharpness
expressed as a number of lines per unit length.
When referring to plotters, addressable
resolution means the smallest move the plotter
can make programmatically.
RS-232-C interface
A serial interface
standardized by the Electronic Industries
Association Standard RS-232-C.
serial interface
A serial interface uses a
single data line to transfer data bits
sequentially between devices. RS-232-C is a
serial interface.
Содержание C2858A
Страница 125: ...7 10 Adjustments Calibrations Notes ...
Страница 155: ...9 4 Product History Notes ...
Страница 160: ...10 5 Parts and Diagrams Illustrated Parts Breakdown Stand Assemblies 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 3 5 3 3 3 3 3 9 9 C C2858 1 1 ...
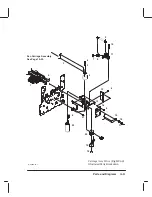
Страница 164: ...10 9 Parts and Diagrams Illustrated Parts Breakdown C2859A Electronics Enclosure C C2858 3 1 ...
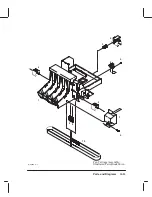
Страница 166: ...10 11 Parts and Diagrams Illustrated Parts Breakdown C2858A Electronics Enclosure C C2858 4 1 ...
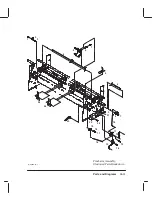
Страница 176: ...10 21 Parts and Diagrams Illustrated Parts Breakdown Service Station Assembly 1 2 3 4 5 6 C C2858 9 1 7 8 9 10 11 12 ...
Страница 180: ...10 25 Parts and Diagrams 1 3 Illustrated Parts Breakdown Pen Carriage Assembly 6 C C2858 11 1 5 7 2 8 9 2 4 5 10 ...
Страница 182: ...10 27 Parts and Diagrams Illustrated Parts Breakdown Paper Drive Assemblies C C2858 12 1 ...
Страница 184: ...10 29 Parts and Diagrams Illustrated Parts Breakdown Bail and Overdrive Support Assemblies C C2858 13 1 ...
Страница 188: ...10 33 Parts and Diagrams Illustrated Parts Breakdown Starwheel Starguard and Chassis Assemblies C C2858 15 1 ...
Страница 198: ... ...