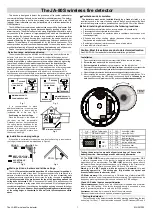
9132A Service
2-10
on,
and
the addresses
on
these chips
go
straight through to the ARAM data
bus.
When the Pod processor accesses
the
ARAM, ARAM-EN is off
and
the ARAM data
is
passed through U94
and
U99 to
the
Pod processor
bus.
U97 and
87 are
used when the Pod is physically capturing ROM addresses.
U39,
US0,
and
U77
are 4-bit counters (for a total of
12
bits) that generate
the address sent to the ARAM
when the
Pod
is
capturing ROM addresses.
These counters
are
preloaded
to
zero and count
up
until
full.
U82, U63,
and
U79 are the address muxes. These ICs control the address
lines to the ARAM. The addresses come either from the address counters
(U39, U50,
and
U77) or from the Pod processor address, depending on the
setting of ARAM enable (ARAM-EN).
U49
and
Ul4
are a
pair of input
ports
that monitor the address counter
(fo
see
where the address stopped if the address counter stopped before
completion),
SSO and SS1 (two sync
state machine indicators),
and
the
sync
pulse from
the sync
counter.
Al12
to the ARAM
is
controlled
by
ARAM-SEL-0
and
ARAM-SEL-1
(when the Pod
is in the
address RAM mode,
ie.,
the Pod is accessing
ROM).
When the Pod
is
operating in the address RAM mode and
an
address RAM clock (ARAM-CLK) is received from the generic PAL (U32),
one edge of ARAM-CLK increments the address counter,
and
the opposite
edge clocks the data into the ARAM.
The write signals
(WU-
and WL-)
and
output enable
(OE-)
are controlled
by
various AND and OR gates, depending
on the
mode of address RAM
enable (ARAM-EN).
If ARAM-EN is true, the address RAM clock
(ARAM-CLK) from U32 controls the write pulses and
any
chip enables,
Address RAM select (ARAM-SEL-) controls the chip enables, and the
read/write pulses control the output enables.
The Sync Module
is
basically a buffer that monitors several lines
on
the
UUT
and
drives the signals up the 50-pin ribbon cable to the Sync Module
connector
(J3).
Eight of
the lines are
data (used for data capture). The
other lines
are
microprocessor-specific status
and
control
lines.
One of the
microprocessor-specific
lines is
always the processor clock (BCLOCK-);
another
is
always the UUT
microprocessor
reset.
U38
is an
input buffer
for the
high speed timing
lines.
Once the lines have
passed through U38,
they
are sent to the Personality Module connector and
to the U44 latch.
U31
and U44 latch
the
condition of these
lines at the
end of
the
sync
pulse. These latches can
then
be read
as an
input port
by
the Pod
processor, which then determines what to do with the information.
When
the Pod is self testing, the SYNC line can
be set
high, forcing the lines to
U31
and U44 to appear transparent, which allows
all
the latched lines to be
accurately read
by
the Pod processor.
The non-latched lines to the
Sync
Module connector control the overdrives.
Overdrive channel
3
high (OVDRV3HI)
and
overdrive channel
3
low
(OVDRV3LO) are controlled
by the
overdrive channel
3
(OVDRVCH3 at
U4D pin
13)
line and timed
by
the Personality Module. The overdrive reset
high (DRV-RST-HI) and overdrive reset low (DRV-RST-LO) lines control
the polarity of
the
reset
signal
sent
to
the UUT reset
line.
Overdrive reset
Содержание 9132A
Страница 53: ...9132A Service 9132A T B 10f 4 E 3 46 Figure 4 1 9132A Final Assembly...
Страница 54: ...9132A Service DETAIL 9132A T8B 2 of 4 Figure 4 1 9132A Final Assembly cont 4 7...
Страница 55: ...9132A Service i g I tg g f 7 im Ly ire 3 9132A T B 3 of 4 48 Figure 4 1 9132A Final Assembly cont...
Страница 56: ...9132A Service MP16 POSITION 1 STRIPE 9132A T B 4 of 4 Figure 4 1 9132A Final Assembly cont 49...
Страница 59: ...9132A Service Hout CEE LE RYT N Bk el FI Soho 9132A 1601 Figure 4 2 A1 Maln PCA 4 12...
Страница 64: ...9132A Service N 2 o 0 mss Ow Dr vd M IO i D SO 0 3 Ct L__A___J 9132A 1607 Figure 4 5 A4 RAM Module PCA 4 17...
Страница 66: ...9132A Service 9132A 24 9132A 28 9132A 32 Figure 4 6 ROM Module Final Assembly 4 19...
Страница 68: ...9132A Service 9132A 1603 Figure 4 7 AS ROM Module PCA 4 21...