38-68
Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3120 for HP Software Configuration Guide
OL-12247-01
Chapter 38 Configuring IP Unicast Routing
Configuring Multi-VRF CE
To configure VRF, you create a VRF table and specify the Layer 3 interface associated with the VRF.
Then configure the routing protocols in the VPN and between the CE and the PE. BGP is the preferred
routing protocol used to distribute VPN routing information across the provider’s backbone. The
multi-VRF CE network has three major components:
•
VPN route target communities—lists of all other members of a VPN community. You need to
configure VPN route targets for each VPN community member.
•
Multiprotocol BGP peering of VPN community PE routers—propagates VRF reachability
information to all members of a VPN community. You need to configure BGP peering in all PE
routers within a VPN community.
•
VPN forwarding—transports all traffic between all VPN community members across a VPN
service-provider network.
Default Multi-VRF CE Configuration
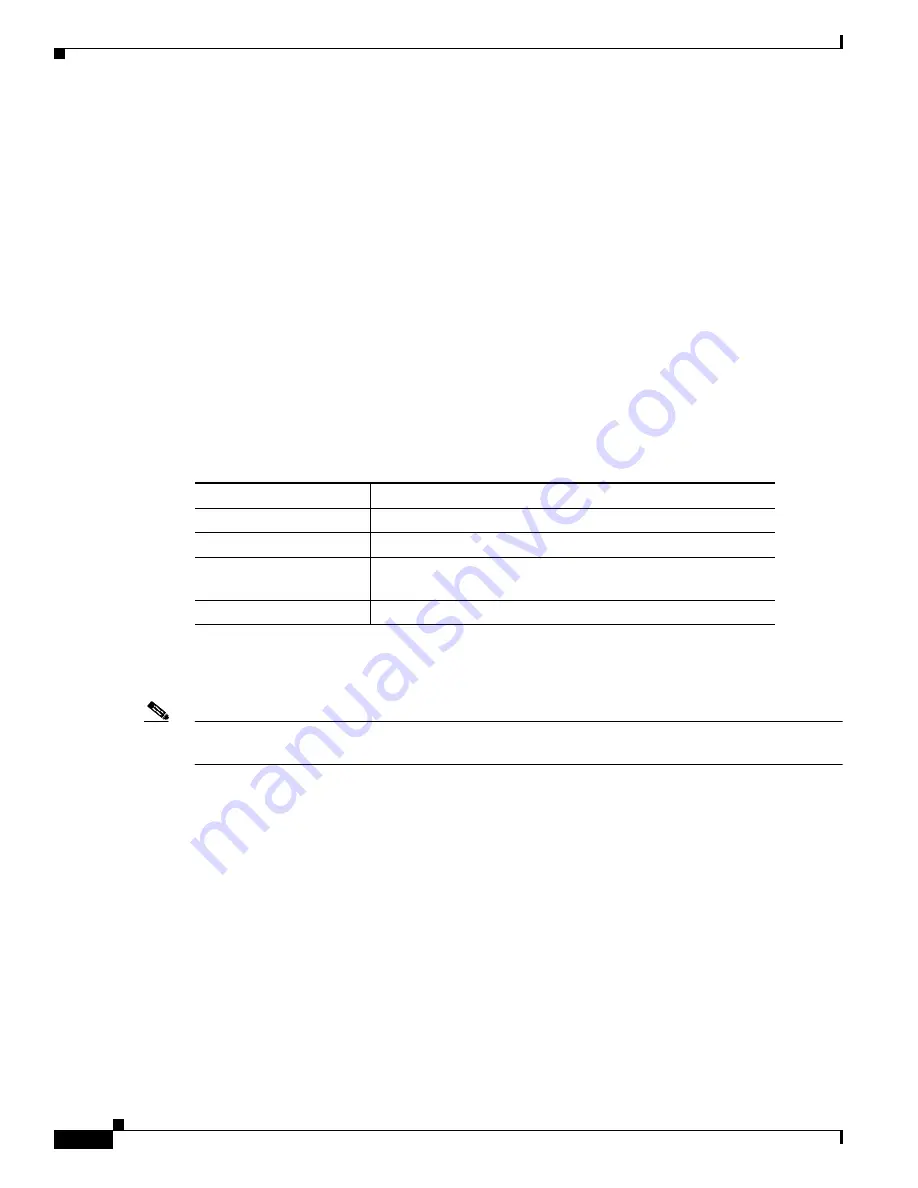
Table 38-12
shows the default VRF configuration.
Multi-VRF CE Configuration Guidelines
Note
To use multi-VRF CE, you must have the IP services or advanced IP services feature set enabled on your
switch.
These are considerations when configuring VRF in your network:
•
A switch with multi-VRF CE is shared by multiple customers, and each customer has its own routing
table.
•
Because customers use different VRF tables, the same IP addresses can be reused. Overlapped IP
addresses are allowed in different VPNs.
•
Multi-VRF CE lets multiple customers share the same physical link between the PE and the CE.
Trunk ports with multiple VLANs separate packets among customers. Each customer has its own
VLAN.
•
Multi-VRF CE does not support all MPLS-VRF functionality. It does not support label exchange,
LDP adjacency, or labeled packets.
•
For the PE router, there is no difference between using multi-VRF CE or using multiple CEs. In
Figure 38-6
, multiple virtual Layer 3 interfaces are connected to the multi-VRF CE device.
•
The switch supports configuring VRF by using physical ports, VLAN SVIs, or a combination of
both. The SVIs can be connected through an access port or a trunk port.
Table 38-12
Default VRF Configuration
Feature
Default Setting
VRF
Disabled. No VRFs are defined.
Maps
No import maps, export maps, or route maps are defined.
VRF maximum routes
Fast Ethernet switches: 8000
Gigabit Ethernet switches: 12000.
Forwarding table
The default for an interface is the global routing table.















































