9-24
Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3120 for HP Software Configuration Guide
OL-12247-01
Chapter 9 Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
Configuring IEEE 802.1x Authentication
IEEE 802.1x Authentication Configuration Guidelines
These section has configuration guidelines for these features:
•
IEEE 802.1x Authentication, page 9-24
•
VLAN Assignment, Guest VLAN, Restricted VLAN, and Inaccessible Authentication Bypass,
page 9-25
•
MAC Authentication Bypass, page 9-26
IEEE 802.1x Authentication
These are the IEEE 802.1x authentication configuration guidelines:
•
When IEEE 802.1x authentication is enabled, ports are authenticated before any other Layer 2 or
Layer 3 features are enabled.
•
If you try to change the mode of an IEEE 802.1x-enabled port (for example, from access to trunk),
an error message appears, and the port mode is not changed.
•
If the VLAN to which an IEEE 802.1x-enabled port is assigned changes, this change is transparent
and does not affect the switch. For example, this change occurs if a port is assigned to a RADIUS
server-assigned VLAN and is then assigned to a different VLAN after re-authentication.
If the VLAN to which an IEEE 802.1x port is assigned to shut down, disabled, or removed, the port
becomes unauthorized. For example, the port is unauthorized after the access VLAN to which a port
is assigned shuts down or is removed.
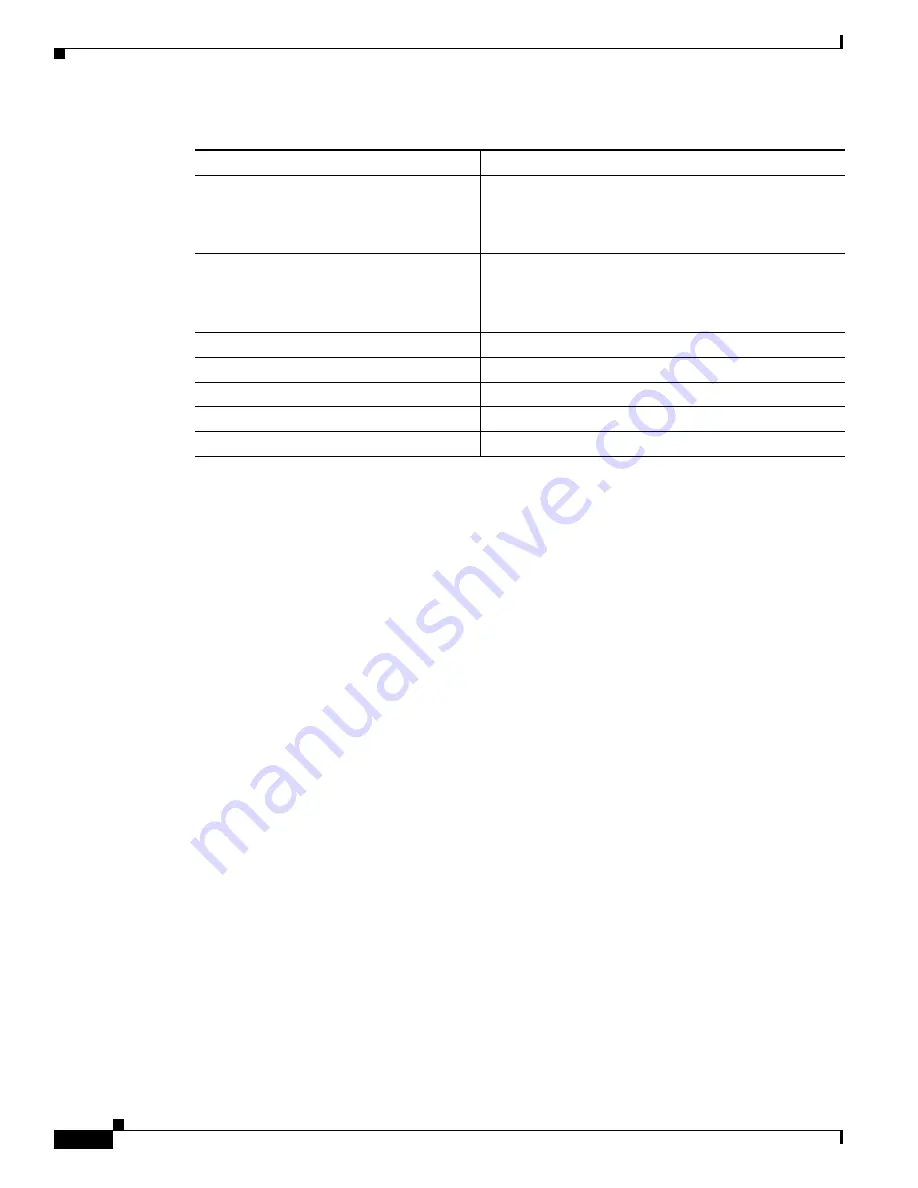
Client timeout period
30 seconds (when relaying a request from the
authentication server to the client, the amount of time the
switch waits for a response before resending the request
to the client.)
Authentication server timeout period
30 seconds (when relaying a response from the client to
the authentication server, the amount of time the switch
waits for a reply before resending the response to the
server. This setting is not configurable.)
Guest VLAN
None specified.
Inaccessible authentication bypass
Disabled.
Restricted VLAN
None specified.
Authenticator (switch) mode
None specified.
MAC authentication bypass
Disabled.
Table 9-2
Default IEEE 802.1x Authentication Configuration (continued)
Feature
Default Setting






























