Commissioning
EL47xx
137
Version: 2.7
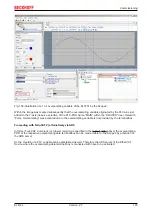
• Actual sampling rate of the ADC (if different from the channel sampling rate)
• Time correction values for run times with different filter settings
• etc.
5.6
Basic function principles
5.6.1
General
The oversampling output terminals EL4712 and EL4732 have the same function. They are therefore referred
to as the EL47xx series below.
The oversampling feature enables the terminal to sample analog output values several times during each
bus cycle on each channel. Both channels are operated with the same oversampling setting.
The EL4712 analog output terminal can be used to output two currents independently with a resolution of
16 bit + sign, i.e. 2
15
= 32767 steps in the range between 0 and 20 mA.
With the EL4732 analog output terminal two voltages can be output independently with a resolution of 16 bit
(65535 steps) in a range between -10 and +10 V.
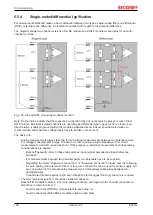
5.6.2
Oversampling
During each bus cycle a conventional analog output terminal processes a set of process data ("sample") per
output channel and outputs an analog output value per fieldbus cycle.
During each fieldbus cycle the EL47xx can handle not just one output value, but a packet of several 16-bit
output values per channel. The EL47xx outputs this set of values at equidistant intervals. The time ratio
between the fieldbus cycle (e.g. 1 ms) and the output period (e.g. 50 µs) is referred to as oversampling factor
(here: 1 ms / 50 µs = 20). The oversampling factor and therefore the EL47xx process data can be configured
via corresponding dialogs.
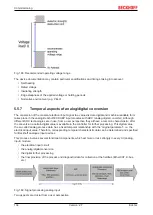
5.6.3
Distributed Clock
Oversampling requires a clock generator in the terminal that triggers the individual data sampling events.
The local clock in the terminal, referred to as distributed clock, is used for this purpose.
The distributed clock represents a local clock in the EtherCAT slave controller (ESC) with the following
characteristics:
• Unit
1 ns.
• Zero point
1.1.2000 00:00.
• Size
64 bit
(sufficient for the next 584 years); however, some EtherCAT slaves only offer 32-bit
support, i.e. the variable overflows after approx. 4.2 seconds.
• The EtherCAT master automatically synchronizes the local clock with the master clock in the EtherCAT
bus with a precision of < 100 ns.
In the EL4732 only the lower 32 bits with are realized (~4.2 seconds).
EtherCAT and Distributed Clocks
A basic introduction into EtherCAT and distributed clocks is available for download from the Beck-
hoff website: the “Distributed clocks system description”.
Sample:
The fieldbus/EtherCAT master is operated with a cycle time of 1 ms to match the higher-level PLC cycle time
of 1 ms, for example. This means that every 1 ms an EtherCAT frame is sent to the EL4732 for transferring
the process data. The local ESC clock therefore triggers an interrupt in the terminal every 1 ms (1 kHz), in
order to read the process data provided by the EtherCAT frame. This first interrupt is called SYNC1.
Содержание EL47 Series
Страница 1: ...Documentation EL47xx Analog output terminal with oversampling 2 7 2020 02 27 Version Date...
Страница 2: ......
Страница 33: ...Mounting and wiring EL47xx 33 Version 2 7 Fig 23 Other installation positions...
Страница 70: ...Commissioning EL47xx 70 Version 2 7 Fig 73 Incorrect driver settings for the Ethernet port...
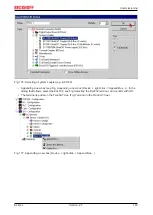
Страница 81: ...Commissioning EL47xx 81 Version 2 7 Fig 92 EtherCAT terminal in the TwinCAT tree left TwinCAT 2 right TwinCAT 3...
Страница 144: ...Commissioning EL47xx 144 Version 2 7 Fig 178 Selecting the EL4732 terminal Fig 179 Terminal in the TwinCAT tree...
Страница 149: ...Commissioning EL47xx 149 Version 2 7 Fig 184 Process data tab SM1 EL47xx...
Страница 156: ...Commissioning EL47xx 156 Version 2 7 Fig 195 Process Data tab adaptation of process data in SM0...