Installation manual
HB-37420-810-01-25F-EN SMX100 Installation manual.docx
Page 238 of 260
Version: 25F
12.3.2 Specification of the functional safety system
Derived from the general danger and risk analysis for the machine, the active safety functions
must be identified and specified.
Active safety functions are, e.g. safely reduced speed under certain system conditions,
monitored stop and standstill functions, area monitoring facilities, processing of monitoring
facilities like light grid, switching mats, etc.
The safety functions must each be delimited and the specific requirements in function and
safety level must be defined.
12.3.2.1
Definition of safety functions
definition of the safety function must:
•
specify the risk to be covered,
•
describe the exact function,
•
list all sensors, command equipment involved,
•
specify the control units and
•
designate the shut-down circuit mentioned.
The definition should serve as basis for the specification of the hardware and software design.
For each of the safety functions defined this way one may need to determine parameters to be
used, like e.g. max. system speed in setup operation, etc.
Examples for safety functions:
SF1: STO (safely switched off torque) to protect against safe starting
SF2: Safe speeds
SF3: Safe positions
SF4.:……
12.3.2.2
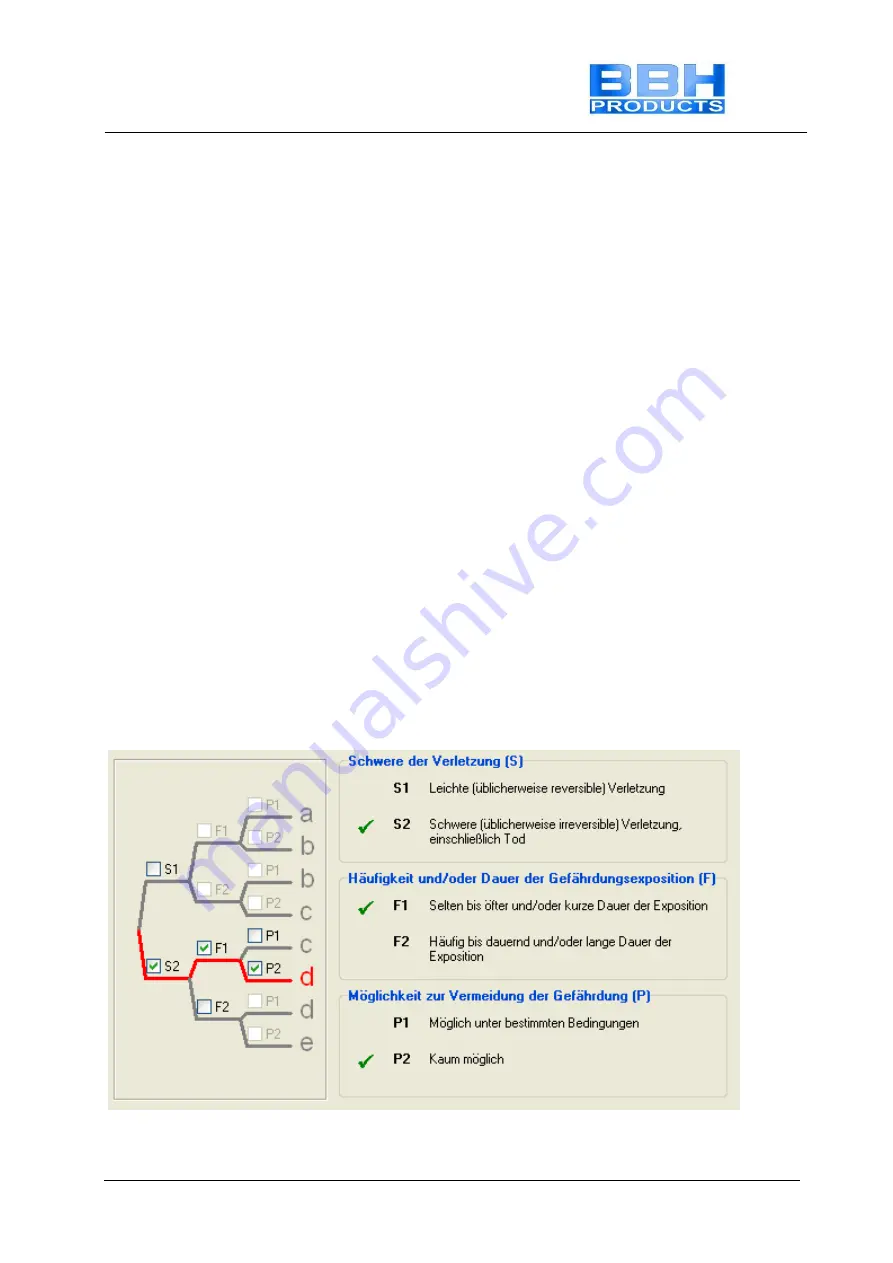
Required performance level (PLr) (additional emergency stop)
The required performance level must now be determined on basis of the safety functions
SF1.... recognized above. The example below shows the decision path.
Example for SF1: Result PF = d (source Sistema)






























