5
E
STABLISHING
ATM C
HANNELS
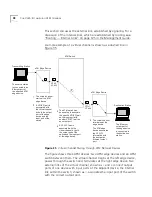
ATM is a connection-oriented transport service, much like a telephone.
Unlike Ethernet, where data is sent out on a common bus, ATM requires
that a path or
virtual channel
be established to carry the call from the
source station to the destination station before data transmission can
begin. A virtual channel may be established either manually through
management or automatically through the processes of
signaling
and
routing
.
This chapter provides basic concepts and information about:
Virtual Channels
VP Tunneling
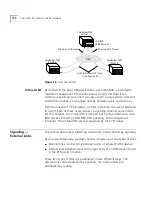
Signaling — External Links
Signaling AAL
Call Admission Control
UNI Signaling 4.0 Features
Routing — Internal Links
Physical-Link Failure Indicator
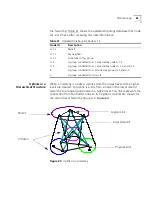
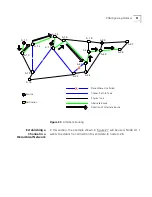
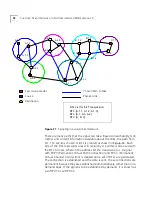
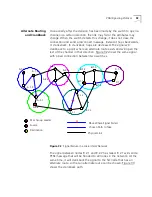
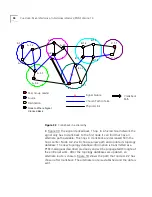
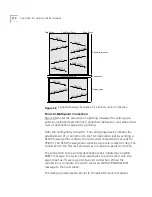
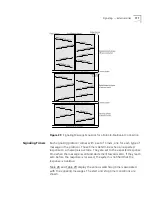
Virtual Channels
A virtual channel
is a communications path that can carry a single call
from the source station to the destination station. The term virtual is used
because the channel does not necessarily correspond to a single physical
line and, in fact, usually passes through many different network devices
and cables before reaching its destination.
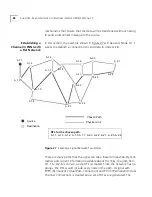
Local Links and
Connections
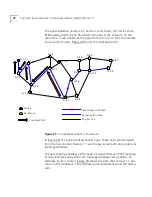
A virtual channel is built from a series of local links of two types:
External links between ports of adjacent ATM devices
Internal links between input and output ports of an ATM device
Содержание CoreBuilder 7000
Страница 12: ......
Страница 30: ...30 CHAPTER 1 ATM NETWORK BASICS...
Страница 32: ...32 CHAPTER 1 ATM NETWORK BASICS...
Страница 34: ...34 CHAPTER 1 ATM NETWORK BASICS Figure 8 LANE Network over WAN...
Страница 96: ...96 CHAPTER 4 PRIVATE NETWORK TO NETWORK INTERFACE PNNI VERSION 1 0...
Страница 184: ...184 CHAPTER 7 LAN EMULATION VERSIONS 1 0 AND 2 0...
Страница 206: ...206 CHAPTER 9 DEVICE MANAGEMENT...
Страница 222: ...222 APPENDIX A TECHNICAL SUPPORT...
Страница 234: ...234 APPENDIX B PROTOCOLS AND INTERFACES...
Страница 238: ...238 APPENDIX C COREBUILDER 7000 FAMILY ATM SWITCH SPECIFICATIONS...
Страница 242: ...242 APPENDIX D SAFETY INFORMATION...