IP Multicast Routing Protocols
501
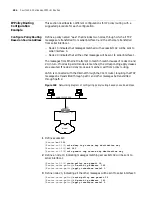
the IP multicast environment, the destination address of a data packet is not one
address but a group, forming a group address. All the information receivers are
added to a group, and once they access the group, data flowing to the destination
address begin to transmit to the receivers of that particular group. All the group
members can receive the data packet. Therefore, to get the data packet, they have
to become group members first. The data packet transmitter is not required to be
a group member. In the multicast environment, data will be sent to all the group
members, and the subscribers who are not group members will not receive the
data packets.
Generally, IP multicast has the following features:
■
The membership of the host group is dynamic .There is no restriction on the
location or the number of members in the host group. Independent hosts
access or leave the multicast group at any time. These members can be
anywhere on the Internet. One host can be a member of several multicast
groups simultaneously.
■
One host can send data packets to a multicast group even though it is not a
group member. When sending the message to all the IP hosts in a multicast
group, it is necessary to send a message to the group address only, just like
unicast.
■
There is no need for the router to save the membership for all the hosts. It is
only necessary to know whether there is any host belonging to a certain
multicast group on the network segment. The physical interface is located on
the network segment. The host can only save the multicast groups it has
joined.
IP Multicast Routing
Protocols
The multicast protocol includes two parts. One part is the Internet Group
Management Protocol (IGMP) acting as the IP multicast basic signaling protocol.
The other part includes the multicast routing protocols such as DVMRP, PIM-SM,
PIM-DM, which implement IP multicast flow routing.
Internet Group
Management Protocol
(IGMP)
IGMP is a simple protocol for the support of multicast transmission. IGMP is a
simple leave/join protocol that allows end-user nodes and their multicast-enabled
routers to exchange messages that describe the wishes of hosts to participate in
multicast groups. It defines the multicast membership establishment and
maintenance mechanism between hosts and routers, and it is the foundation of
the entire IP multicast.
IGMP informs routers about the group members, and enables routers to know the
information about other members within the group through the hosts directly
connected to them. Application programs can learn that information coming from
one data source goes to a specific group. If a LAN subscriber announces that it has
joined a certain multicast group via IGMP, the multicast routers in the LAN
propagate this information by the multicast routing protocol, and finally add this
LAN as a branch to the multicast tree. When the host, as a member of a certain
group, begins to receive information, the routers periodically carry out queries on
this group, and check whether the group members are still participating. As long
as there is a host still participating, routers can continue to receive data. Only after
all the subscribers in the LAN exit this multicast group, are the related branches
deleted from the multicast tree.
Содержание 3036
Страница 1: ...http www 3com com 3Com Router Configuration Guide Published March 2004 Part No 10014299 ...
Страница 4: ...VPN 615 RELIABILITY 665 QOS 681 DIAL UP 721 ...
Страница 6: ...2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE ...
Страница 7: ...I GETTING STARTED Chapter 1 3Com Router Introduction Chapter 2 3Com Router User Interface ...
Страница 8: ...4 ...
Страница 16: ...12 CHAPTER 1 3COM ROUTER INTRODUCTION ...
Страница 34: ...30 ...
Страница 60: ...56 CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM MANAGEMENT ...
Страница 88: ...84 CHAPTER 5 CONFIGURING NETWORK MANAGEMENT RouterA interface ethernet 0 RouterA Ethernet0 rmon promiscuous ...
Страница 98: ...94 CHAPTER 6 DISPLAY AND DEBUGGING TOOLS ...
Страница 110: ...106 ...
Страница 114: ...110 CHAPTER 8 INTERFACE CONFIGURATION OVERVIEW ...
Страница 158: ...154 CHAPTER 10 CONFIGURING WAN INTERFACE ...
Страница 168: ...164 ...
Страница 188: ...184 CHAPTER 13 CONFIGURING PPPOE CLIENT ...
Страница 192: ...188 CHAPTER 14 CONFIGURING SLIP Router ip route static 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 110 0 1 ...
Страница 248: ...244 CHAPTER 16 CONFIGURING LAPB AND X 25 ...
Страница 292: ...288 CHAPTER 18 CONFIGURING HDLC Enable HDLC packet debugging debugging hdlc packet interface type number ...
Страница 320: ...316 ...
Страница 330: ...326 CHAPTER 20 CONFIGURING IP ADDRESS ...
Страница 362: ...358 CHAPTER 21 CONFIGURING IP APPLICATION ...
Страница 374: ...370 CHAPTER 23 CONFIGURING IP COUNT ...
Страница 406: ...402 CHAPTER 25 CONFIGURING DLSW ...
Страница 408: ...404 ...
Страница 452: ...448 CHAPTER 29 CONFIGURING OSPF ...
Страница 482: ...478 CHAPTER 30 CONFIGURING BGP ...
Страница 494: ...490 CHAPTER 31 CONFIGURING IP ROUTING POLICY ...
Страница 502: ...498 ...
Страница 508: ...504 CHAPTER 33 IP MULTICAST ...
Страница 514: ...510 CHAPTER 34 CONFIGURING IGMP ...
Страница 526: ...522 CHAPTER 36 CONFIGURING PIM SM ...
Страница 528: ...524 ...
Страница 532: ...528 CHAPTER 37 CONFIGURING TERMINAL ACCESS SECURITY ...
Страница 550: ...546 CHAPTER 38 CONFIGURING AAA AND RADIUS PROTOCOL ...
Страница 590: ...586 CHAPTER 40 CONFIGURING IPSEC ...
Страница 599: ...IX VPN Chapter 42 Configuring VPN Chapter 43 Configuring L2TP Chapter 44 Configuring GRE ...
Страница 600: ...596 ...
Страница 638: ...634 CHAPTER 43 CONFIGURING L2TP ...
Страница 649: ...X RELIABILITY Chapter 45 Configuring a Standby Center Chapter 46 Configuring VRRP ...
Страница 650: ...646 ...
Страница 666: ...662 ...
Страница 670: ...666 CHAPTER 47 QOS OVERVIEW ...
Страница 700: ...696 CHAPTER 49 CONGESTION MANAGEMENT ...
Страница 706: ...702 CHAPTER 50 CONGESTION AVOIDANCE ...
Страница 707: ...XII DIAL UP Chapter 51 Configuring DCC Chapter 52 Configuring Modem ...
Страница 708: ...704 ...
Страница 762: ...758 CHAPTER 52 CONFIGURING MODEM ...