7.5.1 Application Constants: b
Advanced Operation
7 - 46
User
Change
during
Setting
Factory
Valid Access Levels
User
Constant
Number
Name
g
during
Opera-
tion
Setting
Range
Unit Factory
Setting
V/f
Control
V/f with
PG
Open
Loop
Vector
Flux
Vector
b4-01
Timer function ON-
delay time
×
0.0 to 300.0
s
0.0
A
A
A
A
b4-02
Timer function OFF-
delay time
×
0.0 to 300.0
s
0.0
A
A
A
A
D
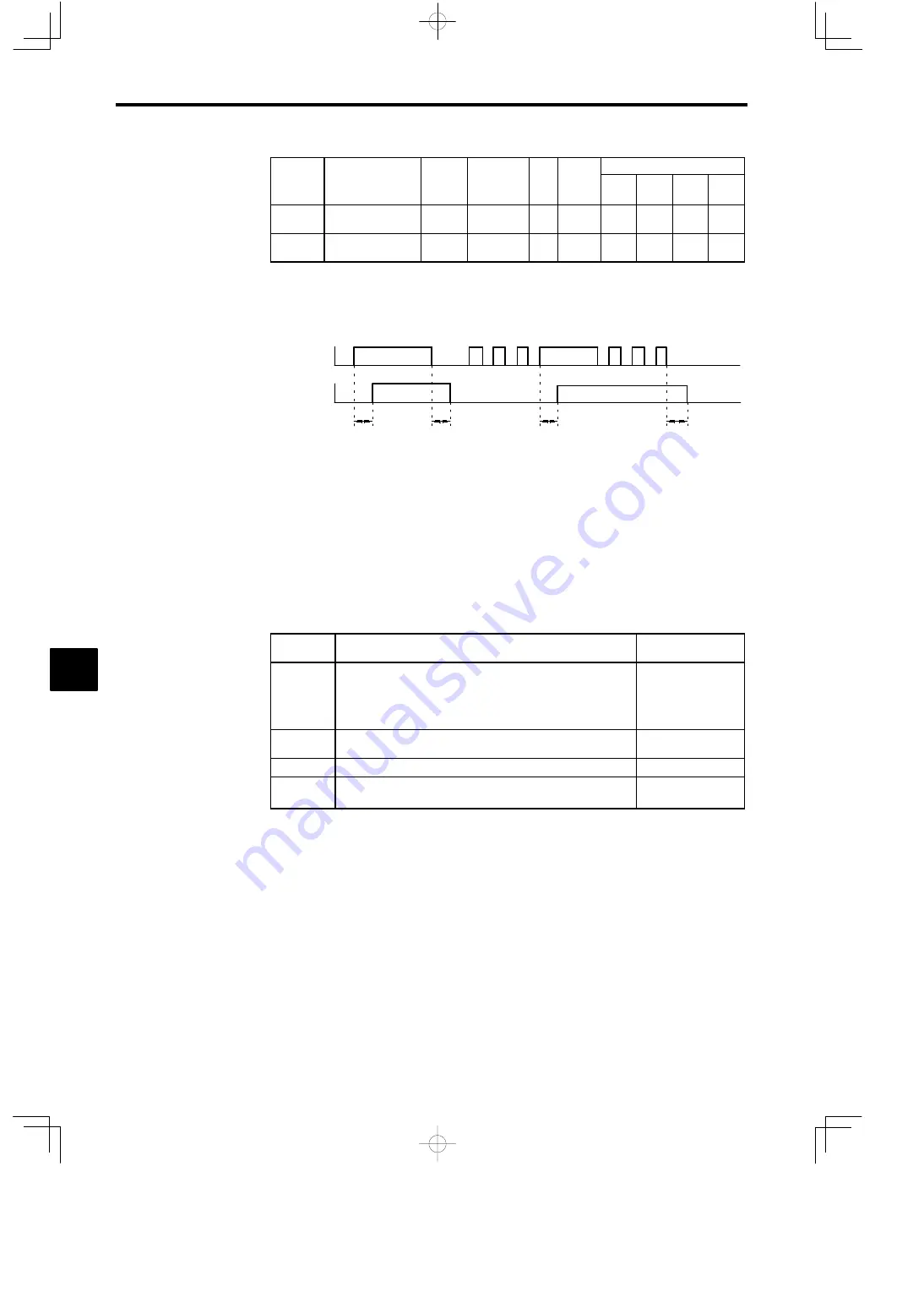
When the timer function input ON time is longer than the value set for b4-01 (timer function ON-delay
time), the timer function output turns ON.
D
When the timer function input OFF time is longer than the value set for b4-02 (timer function OFF-
delay time), the timer function output turns OFF. An operation example of the timer function is shown
in
Figure 7.22
.
Timer function
input
Timer function
output
b4-01
b4-02
b4-01
b4-02
ON
ON
ON
ON
Fig 7.22
Operation Example of Timer Function
J
PID Control Settings: b5-01 to b5-14
The PID control function is a control system that matches a feedback value (i.e., a detected value) to the
set target value. Combining proportional (P), integral (I), and derivative (D) control makes control possible
even for a mechanical system with dead time.
This section explains the PID control applications and operations, along with the constant settings and tun-
ing procedure.
PID Control Applications
Table 7.6 shows examples of PID control applications using the Inverter.
Table
7.6
PID Control Applications
Application
Control contents
Sensors used
(example)
Speed con-
trol
S
Speeds are matched to target values as speed information in a mechani-
cal system.
S
Speed information for another mechanical system is input as target
values, and synchronized control is executed by feeding back actual
speeds.
Tachogenerator
Pressure
control
Pressure information is returned as feedback for stable pressure control. Pressure sensor
Flow control
Flow information is returned as feedback for accurate flow control.
Flow sensor
Tempera-
ture control
Temperature information is returned as feedback to control temperature
by turning a fan.
S
Thermocouple
S
Thermistor
PID Control Operations
In order to distinguish the separate PID control operations (i.e., proportional, integral, and derivative),
Fig-
ure 7.23
shows the changes in the control input (i.e., the output frequency) when the deviation between
the target value and the feedback is held constant.
7
Summary of Contents for VARISPEED-616G5
Page 1: ......






























