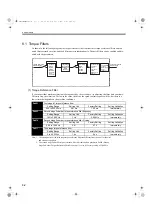
6.2 Specifications and Configurations
6-5
6
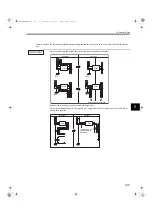
6.2.3 Precautions for Wiring SynqNet Cables
(1) Cable Length
The SynqNet cable lengths are derived from the measured propagation delays during network initialization. This
information is used to determine the spacing between packets for each node. SynqNet networks can have up to 32
nodes and cables can be up to 100 meters in length. By measuring the actual propagation delays and optimizing
the packet spacing, the network performance and actual bandwidth is improved.
Typical CAT5 cable propagation delays are roughly 0.005 microsec per meter. Actual values are affected by
cable construction and will vary, but the variation will be small for any reasonable cable. The propagation delay
can be estimated by a cable propagation velocity of 70% the speed of light, using the formula:
delay = meters * 1,000,000 / (0.7 * 299,722,458)
For example, here are some rough values for various cable lengths:
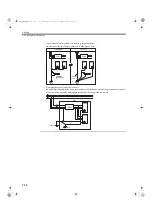
During SynqNet initialization the controller sends a packet to each node, waits for the node to repeat the packet
back, and measures the elapsed time. In ring topologies, the last cable requires the packet to travel around the net-
work and return to the controller. The controller reads the clock values for each measurement packet and stores
the values. The raw time values are then converted into cable length (meters), and the propagation delays are
used to calculate the packet spacing.
The propagation delay measurement is based on the SynqNet clock rate, which is 25MHz (period = 0.040 micro-
seconds). At 25MHz, the clock resolution is 0.040 microseconds, which translates to roughly 8 meters. The accu-
racy is based on the forwarding variations for each node (+/- 1 clock) and the resolution of the propagation delay
timer (+/- 0.5 clocks). The accuracy for each cable can be determined from:
accuracy = ((.020 microsec) + (.040 microsec * nodeCount)) / 2
in terms of meters:
accuracy = ((4 meters) + (8 meters * nodeCount)) / 2
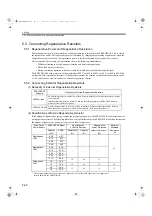
For example, a network with 3 nodes has following cable length accuracies:
Length (m)
Time (
µ
s)
1
0.005
10
0.048
25
0.119
50
0.238
100
0.477
Cable
Reso Variation = Accuracy
0
(.02 + .04)/2 = +/- .03 microsec (+/- 16 meters)
1
(.02 + .08)/2 = +/- .05 microsec (+/- 10 meters)
2
(.02 + .12)/2 = +/- .07 microsec (+/- 14 meters)
SIEPS80000025.book 5 ページ 2004年10月25日 月曜日 午前11時57分