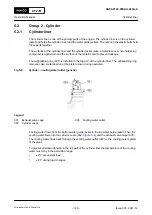
5.2.3
Piston rod gland
The piston rod gland keeps the dirty cylinder oil in the scavenge space and thus prevents
contamination of the bearing oil in the crankcase. Also, the piston rod gland seals the scavenge
air from the crankcase.
Use the sample valve to get system oil samples regularly. The analysis of this oil gives data about
the quality of the cylinder lubrication.
Do regular checks of the leakage oil drain to make sure that oil flows freely. This prevents the risk
of fire.
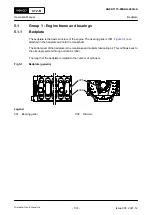
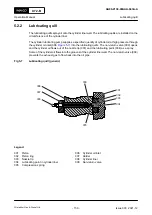
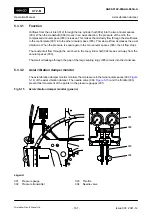
Fig 5-8
Piston rod gland (generic)
001
002
003
004
006
005
007
011
010
009
008
Legend
001
Scraper ring (4-part)
007
Oil drain
002
Housing (2-part)
008
Ring support (3-part)
003
Relief opening
009
Scraper ring (3-part)
004
Neutral space
010
Gasket (4-part)
005
Cylinder jacket
011
Tension spring
006
Support
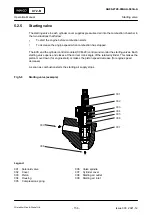
During operation, the two scraper rings (001,
) remove dirty oil from the piston rod. The
dirty oil flows through oil bores and collects in the bottom of the scavenge space. The dirty oil flows
out through the leakage oil drain on the fuel side.
The two gaskets (010) prevent the release of scavenge air into the crankcase.
The oil that flows through the relief openings (003) into the neutral space (004) flows into the oil
drain.
The ring supports (008) hold the scraper rings (009) in position. The scraper rings (009) remove
bearing oil from the piston rod. This bearing oil flows through the oil drain (007) to the crankcase.
The tension springs (011) push the scraper rings (009) and (012) against the piston rod.
X72-B
AA00-2303-00AAA-043A-A
Operation Manual
Piston rod gland
Winterthur Gas & Diesel Ltd.
- 152 -
Issue 003 2021-12