Parameter Description VD520 Series Inverter User Manual
- 176 -
AI Optimize Control Parameter Group
A1-00
Carrier Frequency
0.5kHz~16.0kHz
Model
dependent
○
This function is used to adjust the carrier frequency of the inverter. By adjusting the carrier frequency
can reduce motor noise and avoid the resonance point of mechanical system, reduce the line of floor
drain current and reducing interference caused by frequency inverter.
When the carrier frequency is low, the output current harmonic component increases, motor loss
increases, the temperature rise of the motor increases.
When the carrier frequency is high, the motor loss is decreases, the motor temperature decreases,
but the inverter loss increases, the inverter temperature rise, and the interference increases.
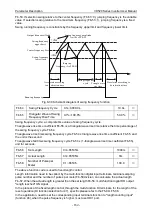
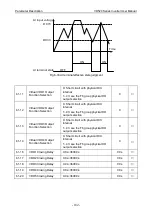
Adjusting the carrier frequency will affect the following performance.
Carrier frequency
Low
→
High
Motor noise
Big
→
Small
Output current waveform
Bad
→
Good
Motor s temperature rising
High
→
Low
Inverter temperature rising
Low
→
High
Leakage current
Small
→
Big
External radiated interference
Small
→
Big
Different power inverter, the factory settings of carrier frequency are different. Although the user can
modify according to the need, but need to pay attention: if the carrier frequency is higher than the
factory value, will lead to frequency inverter radiator temperature rise, at this time the user needs to
use the frequency converter derating, otherwise the inverter has the risk of overheating alarm.
A1-01
Carrier Frequency
Adjustment with the
Temperature
0: No
1: Yes
1
○
Carrier frequency adjustment with the temperature, is refers to the frequency inverter is detected its
radiator at high temperature, reduce the carrier frequency automatically, in order to reduce the
frequency inverter temperature rise. When the radiator at low temperature, carrier frequency is
gradually restored to the setting value. This function can reduce the chance of inverter overheat
alarm.
A1-02
DPWM Switching
Frequency Upper Limit
0.00Hz~15.00Hz
12.00Hz
○
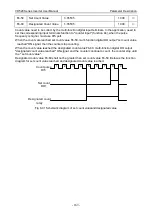
Only valid for V/F control.
The wave mode determined by the asynchronous machine V/F running, which is lower than the value
of the 7 stage continuous modulation mode, on the contrary is the 5 stage intermittent modulation
mode.
The switching loss of the inverter is relatively large when for the 7 stages continuous modulation, but
the current ripple is small; switch loss is small under 5 stage intermittent modulation mode, the current
ripple is larger, may lead to the instability of the motor running at high frequency, generally do not
need to modify.
Please refer to the function code F4-11 about V/F running is not stable, on the loss and temperature
rising of the inverter please refer to the function code A1
–00.