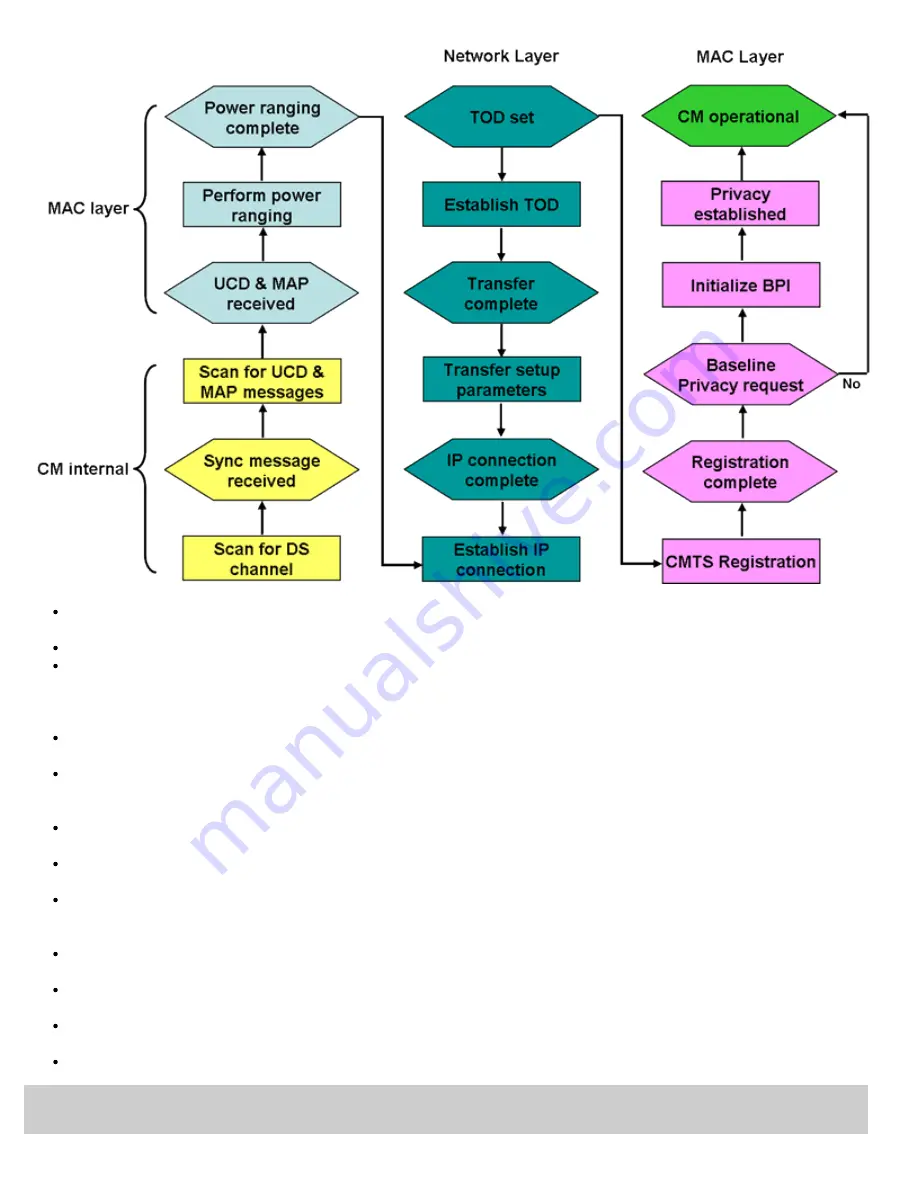
The CM scans the Downstream (DS) spectrum for a valid DOCSIS signal (either 64QAM or 256QAM) - This can be a time
consuming step if the CM is not on a channel.
The CM demodulates the DOCSIS signal and looks for a SYNC message.
The CMTS periodically broadcasts Upstream (US) channel descriptors (UCD) over the DS channel, from which a CM will
learn its assigned upstream operational frequency. The CM in turn scans for these UCD messages, which also tells the CM
how to set up a burst profile (frequency, modulation, and burst parameters). The CM has now established both a US and a
DS frequency.
The CMTS periodically transmits US bandwidth allocation maps (MAP) in shared time slots in the DS direction. The CM
looks for these MAP messages, which list the granted and contended Timeslots (TSs) for US communication.
The CMTS assigns a temporary service identifier (SID) to the CM, which begins a coarse power ranging and time
synchronization process. The first Upstream burst that the CM sends is the initial maintenance - the CMTS responds with
the range-response (RGN-RSP) message for frequency, power, and timing settings.
The CMTS periodically sends keepalive messages to verify link continuity between itself and all CM units in the same
domain. When a CM receives its first keepalive message, it reverts to a fine power ranging.
The CM now forwards a bandwidth request to the CMTS, which in turn forwards a grant to the CM, permitting it to forward
upstream information in allocated time slots.
The CM now makes a DHCP discovery followed by a DHCP request. The CMTS forwards a DHCP acknowledgment from
the DHCP server containing an IP address, a default gateway, the addresses of a TFTP and TOD server, and a TFTP
configuration file name.
The CM now initiates the TOD and TFTP process. From the TFTP server, the CM receives a configuration file containing
QoS, security, applicable frequency assignments, and any new software images.
The CM forwards this configuration file to the CMTS and initiates a registration request. If the configuration file is valid, the
CMTS assigns the CM a permanent SID and registers the CM to online status.
Following registration, the CM optionally initiates the activation of the 56-bit DES encryption algorithm to provide security
between the CMTS and itself over the cable plant.
The CM is now operational.
Note:
DOCSIS specifies that for a system to become functional and operational, the CMTS and CM must
interface with the following mandatory servers;
CX100/110/120/150/180 series e-Manual D07-00-002 Rev B01
Page 29 of 39